Economy
On the clean energy economic opportunity for Indigenous communities in BC
Today in the legislature I rose during question period to ask the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources how he reconciles his government’s claim that it is committed to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples while at the same time introducing measures that will restrict their opportunities for clean energy economic development. I also asked him whether he was willing to instruct B.C. Hydro to declare force majeure on the existing Site C construction contracts, as opposed to the IPP contracts, to save billions upon billions of ratepayer dollars, and instead instruct B.C. Hydro to issue calls for power at market rate for any future power needs.
Below I reproduce the text of our exchange.
Video of Exchange
Question
A. Weaver: Many Indigenous communities in British Columbia anticipated being able to sell surplus electricity to B.C. Hydro. Despite this government’s professed commitment to reconciliation, the decision by B.C. Hydro to cancel its standing offer program has placed these communities in a very difficult position.
As I’m sure the minister is aware, reconciliation is a multifaceted process that involves building genuine, long-lasting economic partnerships with Indigenous communities. Otherwise many such communities will continue to struggle economically. More recently, with the proposed changes to the self-sufficiency clause in the Clean Energy Act, First Nations aspiring to become clean energy producers will be dealt yet another serious blow.
My question is to the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources. How can this government claim that it is committed to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples while at the same time introducing measures that will restrict their opportunities for economic development?
Answer
Hon. B. Ralston: I want to thank the member for Oak Bay–Gordon Head for his question. Let’s begin by remembering that the old government signed insider deals for power at five times the market price. That created a $16 billion obligation owed by British Columbians. That’s $16 billion in unnecessary costs.
We are committed to keeping B.C. Hydro rates low and building a low-carbon economy for people. Maintaining affordable electricity is critical to electrifying our economy and meeting our CleanBC goals. The standing offer program was not compatible with this.
Our government understands — and I acknowledge the import of the member’s question — that many Indigenous communities view small-scale private power as economic development opportunities. Indeed, when we suspended the standing offer program in February 2019, we exempted five projects in development that had significant First Nations involvement.
I agree with the member that it’s important to support Indigenous communities in clean energy economic development. Just last month we announced $13 million for four clean energy projects to help remote communities get off diesel.
Supplementary Question
A. Weaver: Over the last decade, numerous First Nations have banked heavily on clean energy projects as an economic development strategy. Many have entered into agreements with independent power producers to do the same. On Vancouver Island, for example, 13 of the 14 Nuu-chah-nulth First Nations are either current or perspective stakeholders in renewable energy products. The Tla-o-qui-aht Nation has poured over $50 million into clean energy projects and has plans to spend an additional $100 million.
Successful endeavours, such as the T’Sou-ke Nation’s solar farm in the Premier’s own riding, have helped get Indigenous nations off diesel, while others that have received financial backing from the government promise to do the same. For many Indigenous communities across British Columbia, the opportunity to sell excess electricity is a vital component of their future economic plans.
My question, once more, is to the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources. Will the minister instruct B.C. Hydro to declare force majeure on the existing Site C construction contracts, as opposed to the IPP contracts, to save billions upon billions of ratepayer dollars, and instead instruct B.C. Hydro to issue calls for power at market rate for any future power needs?
To remind the minister, market rate is not 20 cents a kilowatt hour. It’s not 15 cents a kilowatt hour. It is a few cents a kilowatt, as is demonstrated worldwide with the price of solar and wind being lower than the price of coal and natural gas combustion in most jurisdictions.
Answer
Hon. B. Ralston: Once again, I’d like to thank the member for Oak Bay–Gordon Head for his question. As a government, we are committed to working collaboratively with Indigenous communities on opportunities for economic development. We consulted widely, including engagement with Indigenous nations, on the Comprehensive Review of B.C. Hydro: Phase 2 Interim Report, which includes the proposal on the self-sufficiency requirement.
I think it’s important to note that the changes that we are proposing will not happen overnight. They will allow B.C. Hydro to consider out-of-province energy, as one option — one option among many — to providing clean and affordable energy, as part of their next 20-year plan. These changes support our climate plan, CleanBC, and they allow B.C. Hydro to continue purchasing power from First Nations-owned projects.
My ministry has a wide range of programs that support Indigenous communities to transition to clean energy and improve energy efficiency. For example, we’ve invested $5 million in the B.C. Indigenous clean energy initiative. This initiative supports community clean energy projects. I appreciate the member’s questions on this important topic. Our government will continue to work with Indigenous communities to identify clean energy opportunities.
Socially & Environmentally Responsible Corporations & Investing: The Opportunity
There is a coming paradigm shift around the purpose of investment and businesses. The last decade has seen growing pressure on corporations to consider the environmental, social, and governance consequences of their investment and management decisions. This more holistic view of the corporation is a necessary and positive development. Corporations do not exist in a vacuum; the societies in which they conduct business are indispensable sources of their success and vitality. Accordingly, corporations have duties to both their shareholders and the societies in which they are embedded. By incorporating these other considerations into their decision-making corporations will not only provide many societal benefits but will enhance profits at the same time.
Increasing numbers of Canadians are coming to believe that companies should stand for something more than profit. Over half of Canadians now lean towards purchasing products from businesses that align with their worldview. Some of this change is likely being driven by the values and interests of millennials and gen-z who make up a growing share of the population. A recent survey by Deloitte provides interesting and important insights into the priorities of these two generations. When asked to identify the three issues they believed to be most important, health care and disease prevention, climate change, unemployment, and income inequality all ranked higher than economic growth.
There are signs that the private sector may be shifting towards more holistic governance models. Many companies are attempting to align their brands with shifting consumer preferences and nascent corporations embrace socially and environmentally conscious business models. In Europe, over two-thirds of the start-ups at the Slush 2019 conference were classified as purpose driven companies, defined as corporations that include one or more of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals as an integral component of their operations, an increase of about 7% from 2014.
However, actions taken by the state can help to accelerate the shift towards corporations with a defined social purpose. By creating the right regulatory and policy frameworks, government can incentivize socially responsible investment. One step in this direction is the BC Government’s recently announced regulations around benefit companies. Canadian corporate law does not have a formal doctrine recognizing shareholder primacy. However, the new legislation and corresponding regulations will empower corporations to continue addressing pressing social and environmental issues as they scale their operations and make it easier for investors to choose companies that align with their values.
In the future, another avenue that the province could consider promoting to encourage investment with the potential to generate positive social returns are community investment co-ops (CICs). CICs are capital pools that provide residents of a specific region or locality with the opportunity to invest some of their money in local businesses. Individual investors typically elect the fund managers themselves to ensure that the investments made through the vehicle are consistent with their priorities and values. Through CICs, residents can become directly involved in economic development projects within their communities.
Ample capital already exists within the province which could be harnessed by CICs. Each year, millions of dollars exit British Columbia to be invested in other jurisdictions. If the province established a structure designed to incentivize investments into CICs, some of this capital could be redirected into local businesses. At a time in which rural regions in BC are experiencing economic stagnation, CICs could be used to reinvest money generated through regional economic activity into local corporations and start-ups, helping to stimulate rural economies.
Several CICs already exist within BC including the Vancouver Island CIC, the East Kootenay CIC, and the West Kootenay Boundary Investment Co-Op. Some have already received financial support from the government. However, there are a number of legislative and regulatory changes open to the government which could be used to make these investment vehicles more attractive to British Columbians. Some options include creating a tax credit for investors and amending the securities act to make it easier for CICs to generate larger capital pools for investment.
The adoption of a legislative and regulatory framework designed to popularize CICs would not be without precedent. Other jurisdictions have successfully introduced programs centered around social finance, including other Canadian provinces. In 1993, Nova Scotia introduced the Equity Tax Credit which allows residents to claim a tax credit on investments made into provincially based businesses. Six years later, the province created the Community Economic Development Investment Funds (CEDIF) program in an attempt to encourage wider adoption of the tax credit. The program offers a streamlined application process for those seeking to establish a CEDIF and allows investors to claim an income tax credit on their investments in the vehicle. By 2013, Nova Scotians had established 47 CEDIFs which had contributed over $56 million in financing to local businesses, some of which were mission-oriented corporations dedicated to social and environmental causes.
When provided with the opportunity to pursue business models that have the potential to generate positive social and environmental outcomes, many individual investors and nascent corporations will choose to do so. As society begins to redefine its expectations of corporations, the province has the chance to become a world leader in the movement towards socially responsible business. The recently introduced legislation and regulations around benefit corporations represent a positive step in this direction but the province should not stop there.
Effective today, BC businesses can now incorporate as Benefit Companies
In May 2019, my private Member’s bill: Bill M209: Business Corporations Amendment Act, 2019 received royal assent but required an Order in Council to become enacted. That happened today. I’m delighted to report that effective immediately, the province is now officially the first jurisdiction in Canada to allow companies to incorporate as benefit companies.
As you will see from the government press release (that I reproduce below) I was pleased to sponsor this bill and to collaborate with government to see it become the first ever opposition private members’ bill passed into law in B.C. Our province is home to incredibly innovative companies that want to play a larger role in addressing the challenges and opportunities we face. This legislation helps position our province to be a leader on the cutting edge of global economic trends. By becoming the first jurisdiction in Canada to create benefit companies, B.C. can position our economy for success as we work to recover from the impacts of COVID-19 and beyond.
My bill amended the Business Corporations Act to create a new Part 2.3 that enabled companies to become benefit companies. These companies will have to meet certain requirements, including:
- Committing in their articles to operate in a socially responsible and environmentally sustainable manner, and to promote specific public benefits;
- The directors must act honestly and in good faith to pursue public benefits and consider the interests of persons affected by the company’s conduct
- Reporting publicly against an independent third party standard.
The choice to become a benefit corporation status is completely voluntary and has no impact on other existing corporations, other corporate forms, taxes or government regulation
It’s generally recognized that Canadian corporate law does not have a strict “shareholder primacy” rule as the US does, so directors of companies in Canada have more discretion to pursue a broader mandate beyond maximizing shareholder profits. However, this legislation was needed to
- Provide clarity for directors and shareholders about the nature and mandate of the company – avoid the risk of a shareholder challenge regarding the director’s duties;
- Provide certainty for impact investors of the nature and mandate of the company;
- Enable companies to attract capital while being true to their mission as they grow;
- Protect the vision of the founders of benefit companies from shareholder challenges;
- Provide a simple framework for companies to adhere to that is legally and commercially recognized.
This legislation also encourages more companies to pursue a socially responsible and environmentally sustainable approach to business, creating beneficial outcomes for society as a whole and leveraging the power of business to help us to tackle significant social and environmental challenges.
Below I reproduce government’s press release issued today. I am grateful to the Minister of Finance, the Legislative drafters, and Sarah Miller, a researcher in the BC Green Caucus, that I worked closely with in developing this legislation.
Government Press Release
New business option empowers companies to give back
For Immediate Release
2020FIN0038-001197
June 30, 2020
Ministry of Finance
VICTORIA – Through historic and collaborative legislation, British Columbia is the first province in Canada to create the option of benefit companies, a new way to do business that benefits people, communities and future generations.
“As government, we’re proud to support B.C. businesses that not only want to do well for their stakeholders, but also give back to their communities in important ways,” said Carole James, Minister of Finance. “By providing the framework through legislation, benefit companies will help propel B.C.’s economy into the future, grounded by the values and beliefs that define us as British Columbians. This is especially important now, as we work to build back better from the impacts COVID-19. I want to thank independent MLA for Oak-Bay Gordon Head Andrew Weaver and my colleagues in the third party for being champions of this new business structure from day one.”
Changes to the Business Corporations Act give British Columbians a new option when choosing a corporate structure for their business. A benefit company is a for-profit corporation committed to conducting its business in a responsible and sustainable manner, as well as promoting public benefits in addition to serving the interests of its shareholders. For example, the benefits could be artistic, charitable, cultural, economic, educational, environmental, literary, medical, religious, scientific and/or technological.
“I was pleased to sponsor this bill and to collaborate with government to see it become the first ever opposition private members’ bill passed into law in B.C.,” Weaver said. “Our province is home to incredibly innovative companies that want to play a larger role in addressing the challenges and opportunities we face. This legislation helps position our province to be a leader on the cutting edge of global economic trends. By becoming the first jurisdiction in Canada to create benefit companies, B.C. can position our economy for success as we work to recover from the impacts of COVID-19 and beyond.”
A business that becomes a benefit company must:
- specify its public benefit goals in its articles of incorporation, allowing investors to determine if the stated public benefit aligns with their investment and social goals;
- complete and publish an annual benefit report assessing the company’s performance in its promotion of its stated public benefits;
- compare its progress against an independent, third-party standard;
- share the report publicly by making it available at the company’s records office and on the company’s website, if it has one; and
- require the company’s directors to balance the commitments in the benefit provision with their duty to act in the best interests of the company.
“Our work to expand and modernize BC Registries has played a key role in bringing this exciting legislation to life,” said Anne Kang, Minister of Citizens’ Services. “Allowing businesses to register as benefit companies gives them more tools to help improve our communities and the well-being of people. This initiative is another step forward in our work to deliver modern, reliable and easy-to-access services for British Columbians, where and when they need them.”
These amendments ensure that B.C. companies committed to considering the impact of their decisions are able to balance the needs of their shareholders with the values of British Columbians.
The values of collaboration, partnership and public good are foundational to the Confidence and Supply Agreement with the BC Green Party caucus, and it continues to provide the basis for a strong, stable government for British Columbia. By working together, progress continues to be made on shared priorities, like climate change, tackling the housing crisis and building a sustainable economy that works for everyone.
Quick Facts:
- Benefit companies were first introduced in 2010 in the United States and are now possible in 35 U.S. states, as well as Italy and Colombia.
- On May 16, 2019, the Business Corporations Amendment Act (No. 2) received royal assent.
- This is the first private member’s bill from an opposition party to be passed directly into law in B.C.
Learn More:
To learn more about the amendments, visit: www.bclaws.ca/civix/document/id/bills/billsprevious/4th41st:m209-1/search/CIVIX_DOCUMENT_ROOT_STEM:(Business%20Corporation)%20AND%20(benefit)?1#hit1
Ongoing regulatory inconsistencies facing Pacific Booker’s Morrison mine project
Yesterday I published a blog post detailing the apparent regulatory inconsistencies facing the advancement of Pacific Booker’s Morrison Mine project. Today during question period I rose to explore this issue further with the Minister of Environment. Today’s question built upon an initial question I asked the Minister of Energy Mines and Petroleum Resources on March 5, 2020.
Below I reproduce the text and video of our exchange.
Video of Exchange
Question
A. Weaver: On March 5, I asked the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources a question concerning regulatory inconsistencies in the provincial government’s handling of Pacific Booker’s proposed Morrison mine. I’d like to explore this a little further.
In 2015, after reviewing the project for a second time, the Ministry of Environment issued a section 17 order that the project undergo further assessment. Despite numerous exchanges with the environmental assessment office and the completion of an in-depth study of Morrison Lake, Pacific Booker has been unable to clarify the precise nature of what is actually required in the section 17 order. For Pacific Booker, this order has been tantamount to a rejection of its project without the ministry formally saying no.
Government recently amended the environmental assessment process to provide certainty of process and clarity of regulatory considerations. When presented with an application for an environmental assessment certificate, the minister is given three options under the 2018 Environmental Assessment Act:
(1) grant the certificate,
(2) grant the certificate with conditions attached or
(3) reject the project.
Pacific Booker’s treatment doesn’t align with the new assessment standards. They’ve been given the opposite of regulatory certainty, and their project has been shunted off for a further assessment. My question is to the Minister of Environment. Considering the recent changes to the environmental assessment process, will he amend the 2015 order to clarify the nature of the work required by Pacific Booker Minerals?
Answer
Hon. G. Heyman: Thank you to the member for the question. I recall the question to my colleague, the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources, in March quite well. As the Minister of Energy and Mines said at the time, he and I can’t speak to the specifics of why the old government made the decision that it made with respect to the proposed Morrison mine.
The member is also correct. We made significant changes to the Environmental Assessment Act through revitalization, and we’re proud of that as our government. We brought new transparency to the act. We’ve included engagement of Indigenous peoples and local communities at the front end, and we have taken steps to ensure that good projects that respect the environment, that respect Indigenous peoples and that respect the public can be approved more quickly with greater certainty.
However, with regard to Pacific Booker, the member is correct. Under the old act, the decision was made to require additional information from the proponent before a final decision on the proposal was made.Under the new legislation or the transition regulation, there is no ability to take a project like Morrison that has proceeded this far down the process and transfer it to the provisions of the new act. But it’s my understanding that the company is currently working through the required regulatory process for further assessment in tandem with the environmental assessment office.
Supplementary Question
A. Weaver: Thank you, Minister, for your answer. I think the minister may have missed the point. Pacific Booker doesn’t know what the section 17 order does because what they’re supposed to do has not been conveyed to them with any certainty. So they are left with an uncertain order, of which they don’t know how to respond. So it’s not possible for them to move through the regulatory process when that process has not been defined in which they could go.
They have conducted detailed assessments of Morrison Lake and its internal wildlife, including measuring water quality and lake mixing patterns as well as investigations into fish habitat and spawning patterns. They have pledged to use cutting-edge technology to reduce groundwater seepage from the tailings storage facility. They’ve even completed a request, and they were the only one asked to do so, to comment on the implications of Mount Polley for their tailings management.
Throughout the protracted environmental assessment process, Pacific Booker has stated its preference to use local suppliers and to hire local workers. The project would generate over 1,000 jobs in the region near Smithers, and it would provide millions of dollars in tax revenue. At a time when the provincial economy is reeling due to the efforts of COVID-19, the project would give that region a much-needed economic boost.
My question, again, to the Minister of Environment is this. Given the extensive work undertaken by Pacific Booker Minerals to examine and reduce the environmental impact of the potential Morrison mine project and the potential economic benefit to the province, will this government commit to ensuring that the company receives a timely, unbiased review of the latest proposal, and in particular, is given clear instructions from your office so that it knows what boxes need to be ticked so that they can follow due process, rather than second-guessing certain people who haven’t made that very clear?
Answer
Hon. G. Heyman: Thank you again to the member for the supplemental question.
The company, of course, has to provide some very specific additional information that was required under the order. The order was specific. Some examples of the type of additional information required are sockeye salmon use of Morrison Lake, upper and lower Tahlo Creek and the Morrison River, hydrogeological and groundwater data for areas between the mine and Morrison Lake and further engagement with the Lake Babine Nation and other impacted First Nations.
I’m advised that the company made its latest submission to the environmental assessment office in December and that environmental assessment office staff met with the company this past February as additional information was required from the company. It is certainly not the intention of our government to make proponents guess at what is required. I checked with the environmental assessment office, and my understanding is that staff there are working to help answer any questions that the proponent has with respect to the information required.
I’m advised that the company plans to provide an update to the environmental assessment office regarding their next steps, and the environmental assessment office will be very happy to assist them in a timely answering of the questions required by the order. As minister, I assure that when the application is complete and ready for reconsideration, it will be considered in a timely manner.
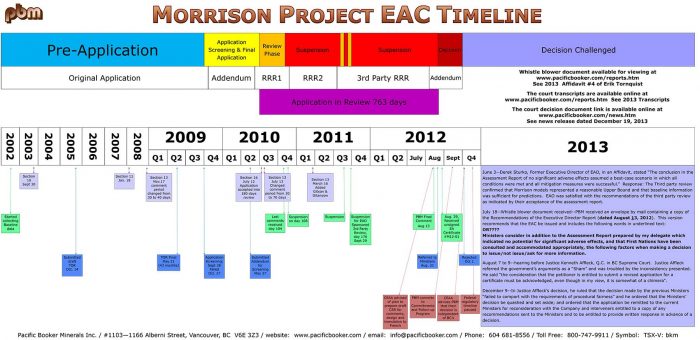
Pacific Booker Minerals and their quest to develop Morrison Mine near Smithers
In 2002, Pacific Booker Minerals began the formal environmental assessment process required to obtain ministerial certification for Morrison Mine, their proposed copper and gold mine near Smithers, BC. A decade later, after $10 million worth of consultations, meetings, and assessments, the company decided to proceed to the next stage of the certification process in which the Environmental Assessment Office (EAO) submits a formal environmental assessment report to the relevant ministers via the executive director. At the time of submission, all indications were that the mine would receive approval. EAO assessment reports had given the project a clean assessment and the company had proposed to undertake measures unprecedented in the copper mining industry to address the project’s environmental risks. Despite the positive environmental assessment, the Executive Director of the EAO chose to recommend that the project be rejected, advice which was followed by Environment Minister Terry Lake. The decision to reject proposed project was ostensibly made due to ongoing concerns about the effects of the project on local salmon populations and water quality in Morrison lake, among other things.
Yet the decision to reject the project on environmental grounds should raise immediate questions about why this project was nixed and not others, given the BC Liberal government’s environmental record in the mining sector. As highlighted in my question posed to the Minister of Energy, Mines, and Petroleum Resources in the House back in March, this is the same government that went to Ottawa in 2014 to lobby the federal government to approve the Prosperity mine, a project that had received two negative assessments by federal review panels. Moreover, the BC Liberals presided over a compliance and enforcement regime that the auditor general described as “inadequate to protect the province from significant environmental risk” and unfunded taxpayer liabilities in the mining industry were estimated at $1.4 billion as of 2017.
The decision to reject the project had serious repercussions for Pacific Booker. Their share price plummeted from $14.95 to $4.95 in one day and many investors lost their life savings. What’s more is that the Ministry failed to inform Pacific Booker of its intention to issue an adverse recommendation and did not provide the company with an opportunity to respond to it, conduct which deviated from the standards outlined in their own user guide.
Rather than face the prospect of beginning the assessment again Pacific Booker decided to enter into litigation with the government over its decision to reject the project. Among other things, the case was fought over whether the Ministry had violated standards of procedural fairness by denying the company the chance to respond to the Executive Director’s recommendation. During the court proceedings, Justice Affleck would describe the environmental assessment process as a “sham” and accuse the province of repeatedly “moving the goalposts” during the assessment process. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the Supreme Court would rule in favour of Pacific Booker, writing that the firm “ought to have been entitled to know at least the essence of the adverse recommendations and ought to have been entitled to provide a written response”.
The ruling from the Supreme Court quashed the decision to reject the mine and ordered the project to be reconsidered by the government. Yet once again, the government elected not to approve the mine and ordered that the project undergo further assessment with the requirement that additional information be collected. Despite repeated exchanges with the environmental assessment office in which Pacific Booker attempted to determine what exactly this additional information is, the firm has been unable to obtain a clear answer from government officials, placing the project in a state of limbo. As of early 2020, the company was still in the process of working through the Supplemental Application Information Requirements with the EAO, in accordance with the order issued by the Ministers.
Based on the previous government’s environmental record in the mining sector (raised earlier), there has been speculation that the decision to reject the mine had little to do with environmental concerns and everything to do with political calculation. What could these political concerns have been? It is difficult to determine one single political factor that led to the decision around the Morrison mine but several interrelated developments which are explored in more detail below provide insight into the political circumstances surrounding the project.
Two ‘Final’ Environmental Assessment Reports
In 2013, before the court proceedings began, a whistleblower provided Pacific Booker with a copy of an assessment report on the Morrison mine dated August 21st. The report contained notable differences from its final version that was ostensibly used to inform the government’s final decision and released publicly. Subsequent emails obtained by the company through a Freedom of Information (FOI) request have revealed that the Minister had requested changes to the original document which should raise questions about the political neutrality of the decision to reject the mine. On July 16th 2014, the project assessment director Chris Hamilton wrote to Sarah Bevan: “Hmm, I recall the first PBM knew about the no was a phone call on Oct 1, a Monday. Could you be thinking about the two versions of the recommendations? One was dated Aug 21, the date of the referral and then Minister Lake had asked for changes to that doc, so the second was dated Sep 20. Could that be it?”
To date, the Ministry has denied any allegations of political interference in the environmental assessment process. In his affidavit in Pacific Booker v British Columbia, David Sturko claimed that: “The clarifications requested by Minister Lake were (a) correction of a factual error relating to the project’s anticipated contribution to Provincial Gross Domestic product, and (b) more specificity regarding the nature and basis of the additional factors I cited in my recommendations at the end of the document”.
The Relentless Pursuit of LNG
For some time, the Lake Babine Nation has been opposed to the Morrison mine. Members of the community have expressed significant concerns about the effects of the project on local salmon populations which are important to the nation for cultural, historical, and economic reasons. When the decision was made to the reject the project, a secondary justification that the director of the EAO provided in his report was the “moderate to strong” strength of the Lake Babine Nation’s claim to aboriginal title in the area. Based on the strong opposition of the nation to the project, it is possible they would have pressed an aboriginal title claim in court to delay or block the project from proceeding.
At the time the project was rejected this appeared to be the only consideration that the province had given to First Nations issues. However, subsequent developments have made political conflict involving the Lake Babine Nation increasingly salient to the delayed progress on the project. In 2016, the Lake Babine Nation cautioned the province that their cooperation on major LNG projects, including the Prince Rupert Gas Transmission line, could be contingent upon the government not overturning its decision on the Morrison mine. Referencing the pipeline, Chief Wilf Adam was quoted in Business in Vancouver as saying: “If they overturn or change their decision in favour of PBM to start this mine, then all gloves are off – and any agreement we made with the province,”.
Raising the issues that have emerged around the Lake Babine Nation is in no way meant to diminish the obligation that the government has to undertake meaningful consultation with indigenous communities before projects can proceed. Resource development needs to be based on equal partnership between all parties with interests at stake in proposed projects. Rather, highlighting the political conflict involving the Lake Babine Nation is meant to bring attention to the fact that decisions involving the Morrison mine may have been influenced by political calculation that had little to do with the proposed project itself.
Project Suspension
Just before the Ministry was ready to release the order requesting further assessment, the Morrison mine was placed under suspension after the Mount Polley Mine disaster, pending the outcome of a provincial review. At the time, the Pacific Booker was the only project that was placed under suspension while the government was investigating the Mount Polley incident. To date, no explanations have been given for why the Morrison mine was suspended and not others. The delay would last for approximately one full year before the order was released.
Pipeline Politics
At the time the project was rejected, the BC Liberals were embroiled in a dispute with Alberta over the construction of the Enbridge pipeline where the most contentious issue in negotiations was revenue sharing. The Liberals took the position that BC would need to receive a higher share of the royalties for the amount of environmental risk the province would absorb in order for the pipeline to proceed. However, comments from some observers had implied that taking this stance placed BC in a weak negotiating position due to the BC Liberal government’s poor environmental record. Further compounding the government’s problems was a looming election in which the NDP had attempted to make the Enbridge pipeline an election issue. Then BC NDP leader Adrian Dix had been heavily critical of the government’s environmental record and had accused the BC Liberals of selling out BC’s interests to the federal government and to Alberta.
Towards a Resolution?
While there is no smoking gun which serves evidence that the province had politicized the environmental assessment process, the suspicious circumstantial evidence that suggests otherwise does little to inspire confidence from British Columbians in their government and has damaged the province’s reputation as a good place to do business. Furthermore, the decision to reject the project has had significant ramifications for Pacific Booker and its investors. Small investors in the project have lost their life savings and have been forced to continue to work well into their retirement years. Based on these factors along, this government has a responsibility to ensure that this project is given a fair hearing in what is now effectively its third environmental assessment.