Energy and Mines
Yellowknife and Kelowna wildfires burn in what is already Canada’s worst season on record
I published an article in The Conversation today. It is reproduced below as Facebook appears to be blocking reposting of Canadian news articles.
The Article
The devastating wildfire that destroyed the historic Maui town of Lahaina in Hawaii was still making headlines when the Northwest Territories issued an evacuation order for Yellowknife and British Columbia declared a provincewide state of emergency.
All 22,000 residents of Yellowknife are being evacuated in advance of a wall of flame from out-of-control wildfires converging on the capital city. Yet this isn’t the first time an entire Canadian town has been cleared.
In May 2016, all 90,000 residents of Fort McMurray, Alta., were evacuated shortly before wildfires engulfed 2,400 homes and businesses with a total cost of more than $4 billion.
In 2017 in British Columbia, the wildfire season led to the evacuation of more than 65,000 residents across numerous communities, costing $130 million in insured damages and $568 million in firefighting costs.
Let’s not forget the June 2021 heat dome resulting in temperature records being broken across British Columbia three days in a row. The heat wave culminated in Lytton, a village in the southern part of the province, recording 49.6 C on June 29, the hottest temperature ever observed anywhere in Canada and breaking the previous record by five degrees. The next day, wildfires engulfed Lytton, destroying more than 90 per cent of the town.
Long, hot summer
The summer of 2023 is one for the record books. June and July were the warmest months ever recorded, and extreme temperature records were broken around the world.
By mid-July, Canada had already recorded the worst forest fire season on record. And British Columbia broke its previous 2018 record for worst recorded forest fire season. With several weeks to go in the 2023 forest fire season, more than six times the 10-year average area has already been consumed by wildfires
And yet, this pales in comparison to what we can expect in the years ahead from ongoing global warming arising from greenhouse gas emissions released through the combustion of fossil fuels.
Predicted outcomes
This year’s fire season record will be broken in the near future as warming continues. And once again, it’s not as if what’s happening is a surprise.
Almost 20 years ago, my colleagues and I showed that there already was a detectable human influence on the observed increasing area burned from Canadian wildfires. We wrote:
“The area burned by forest fires in Canada has increased over the past four decades, at the same time as summer season temperatures have warmed. Here we use output from a coupled climate model to demonstrate that human emissions of greenhouse gases and sulfate aerosol have made a detectable contribution to this warming. We further show that human-induced climate change has had a detectable influence on the area burned by forest fire in Canada over recent decades.”
It appears little has been done to prepare rural Canada for what’s in store as governments deal with immediate, rather than transformational approaches to wildfire management.
This, despite the existence of the national FireSmart program designed to assist homeowners, neighbourhoods and communities decrease their vulnerability to wildfires and increase their resilience to their negative impacts.
Forest management practices including forest fire prevention, monoculture reforestation and the use of glyphosate to actively kill off broadleaf plant species, will all have to be reassessed from a science- and risk-based perspective.
Growing number of court cases
Pressure is certainly mounting on decision-makers to become more proactive in both mitigating and preparing for the impacts of climate change.
An Aug. 14 pivotal ruling from the Montana First Judicial District Court sided with a group of youth who claimed that the State of Montana violated their right to a healthy environment.
A similar case brought by seven youth against the Ontario government after the province reduced its greenhouse gas reduction targets has also been heralded as groundbreaking.
As the number of such court cases grow, governments and corporations will need to do more to both protect their citizens from the impacts of climate change, and to aggressively decarbonize energy systems.
I wouldn’t be surprised if the Alberta government is next to be taken to court by youth after Premier Danielle Smith’s outrageous economic and environmental decision to put a moratorium on renewable energy projects.
States of emergency
While attention is currently turned to the evacuation of Yellowknife, it’s sobering to remind ourselves that they are not alone. The village of Lytton, burnt to the ground just two years ago, has been put on evacuation alert as wildfires approach.
Kelowna has just declared a state of emergency as the McDougall Creek fire starts consuming homes in the region. And this, coming on the heels of the 20th anniversary of the Okanagan Mountain Park fire, when more than 27,000 people had to be evacuated and 239 Kelowna homes were lost.
Canadians will take solace as summer turns into winter and the immediacy of our 2023 wildfire situation wanes. Unfortunately, it will be Australia’s turn next to experience the burning wrath of nature in response to human-caused global warming and the 2023 El Niño.
Rather than waiting to respond reactively to the next fire season, proactive preparation is the appropriate way forward. For as the old adage states: an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
Advancing nature based climate solutions: a cautionary tale
In recent years, governments and industry have become more and more interested in supporting so-called nature based climate solutions. So what are such solutions? The Nature Conservancy provides a concise definition: Nature-based climate solutions “are actions to protect, better manage and restore nature to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and store carbon.”
Such solutions aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions (mitigation) fall into two categories: 1) those that the enhance the uptake and storage of carbon within natural ecosystem; 2) those that reduce the emissions of greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide and methane) from natural ecosystems.
While the above definition recognizes the link between natural ecosystems and the global carbon cycle, nature based solutions also play a critical role in climate change adaptation strategies. A more complete definition that includes both their roles has been offered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), and subsequently used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
“Nature-based Solutions are actions to protect, sustainably manage, and restore natural and modified ecosystems that address societal challenges effectively and adaptively, simultaneously benefiting people and nature.“
Below I attempt to highlight the important role that such solutions play in both climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies. But I try to put such solutions in the bigger context of what needs to be done to meet the challenge of global warming. I’ll attempt to outline why governments and industry appear to be so supportive of such solutions, yet point out the danger of over-relying on them.
To be clear, nature-based climate solutions have a crucial role to play. Cumulative anthropogenic fossil carbon emissions from 1750 to 2021 have been 474 GtC (billions of tons of carbon), while deforestation and land use changes have contributed another 203 GtC. That is, anthropogenic disruption of natural ecosystems has accounted for about 30% of historical greenhouse gas emissions, so it seems reasonable to expect nature-based climate solutions to have an important role to play moving forward. But there are limits. In fact, a recent paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences suggested that nature-based solutions could be used to meet 20% of the required emission reductions to be implemented prior to 2050 to keep global warming to below 2°C. I’ve pointed out for years (and summarized these views again recently), that the 1.5°C target was not attainable even when proposed in the 2015 Paris Accord, due to socioeconomic inertia in our built environment, the role of atmospheric aerosols, and potential effects from the permafrost carbon feedback.
Examples of Nature Based Climate Solutions
To start, I thought it would be illustrative to provide a few examples of nature based climate solutions in action. This list is by no means comprehensive, but rather serves solely to give the reader a sense of what such solutions entail.
 The most obvious example of a nature based solution is planting trees. Widespread deforestation, particularly in the creation of pastures for cattle grazing and land for farming or other human uses, has provided the lion’s share of the historical 203 GtC released to the atmosphere. Reforestation (planting trees where they once were) and afforestation (planting trees in places where they weren’t historically present) both have the potential to draw carbon from they atmosphere as they grow. But of course, if we want to use tree planting in carbon budget accounting, we would also have keep track of the carbon released during forest fires.
The most obvious example of a nature based solution is planting trees. Widespread deforestation, particularly in the creation of pastures for cattle grazing and land for farming or other human uses, has provided the lion’s share of the historical 203 GtC released to the atmosphere. Reforestation (planting trees where they once were) and afforestation (planting trees in places where they weren’t historically present) both have the potential to draw carbon from they atmosphere as they grow. But of course, if we want to use tree planting in carbon budget accounting, we would also have keep track of the carbon released during forest fires.
Urban planners also incorporate tree management in their climate adaptation strategies. For example, they recognize that increasing the tree canopy can help keep cities cooler in the summer than they would otherwise be. Homeowners, for example, might plant deciduous trees in their front yard that blocks the sun from their main windows in the summer, but allow the sunshine in during the late fall and winter once the leaves have fallen.
 The use of biochar to enhance the properties of soil has also been proposed as a potential nature-based climate solution. Biochar (a charcoal like substance) is created through a process known as biomass pyrolysis. (high temperature decomposition of plant material). The addition of biochar to agricultural soil leads to enhanced soil carbon uptake and storage, reduced requirement for fertilizer use (and hence reduced nitrous oxide emissions), and improved water use efficiency. Other agricultural nature-based solutions involving tiling practices, crop/grazing rotations, cover crops etc. have also been proposed.
The use of biochar to enhance the properties of soil has also been proposed as a potential nature-based climate solution. Biochar (a charcoal like substance) is created through a process known as biomass pyrolysis. (high temperature decomposition of plant material). The addition of biochar to agricultural soil leads to enhanced soil carbon uptake and storage, reduced requirement for fertilizer use (and hence reduced nitrous oxide emissions), and improved water use efficiency. Other agricultural nature-based solutions involving tiling practices, crop/grazing rotations, cover crops etc. have also been proposed.
 In the coastal ocean, mangroves, salt marshes and seagrass meadows more efficiently capture and store carbon than land based, slow-growing forests. Many of these so called “blue carbon” sinks have been stressed by human activity in research decades and steps have been taken to both preserve and enhance their health and extent. These rich, biodiverse ecosystems also play key roles in climate change adaptation as they serve to protect coastal erosion from storms and sea level rise.
In the coastal ocean, mangroves, salt marshes and seagrass meadows more efficiently capture and store carbon than land based, slow-growing forests. Many of these so called “blue carbon” sinks have been stressed by human activity in research decades and steps have been taken to both preserve and enhance their health and extent. These rich, biodiverse ecosystems also play key roles in climate change adaptation as they serve to protect coastal erosion from storms and sea level rise.
Recognizing the importance of nature-based solutions, the Canadian federal government developed a natural climate solutions fund to protect, enhance and preserves Canada’s biodiverse and carbon rich wetlands, grasslands and forests, in addition to a commitment to plant two billion trees over a ten-year period.
What’s required to stabilize atmospheric temperature
As most everyone is aware, the goal of the internationally-negotiated Paris Agreement is to limit global warming to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels while pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 °C. Yet we’ve known for more than 15 years that such a target would ultimately require rapid decarbonization and the introduction and scale-up of negative emission technology. In a paper entitled Long term climate implications of 2050 reduction targets that we published in 2007, we note in the abstract (and discussed below):
“Our results suggest that if a 2.0°C warming is to be avoided, direct CO2 capture from the air, together with subsequent sequestration, would eventually have to be introduced in addition to sustained 90% global carbon emissions reductions by 2050.“
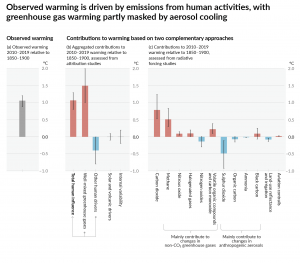
Earth has already warmed by ~1.1-1.2 °C since preindustrial times and if worldwide fossil fuel combustion was immediately eliminated, the direct and indirect net cooling effect of atmospheric aerosol loading would rapidly dissipate through gravitational settling and precipitation scavenging of these aerosols. As such, the source of the ~0.5 °C aerosol cooling realized since the preindustrial era would be eliminated (see Figure 1), thereby taking the Earth rapidly to ~1.6-1.7 °C warming. The Earth would warm further as we equilibrate to the present 523 ppm CO2e (NOAA 2023) greenhouse gas loading in the atmosphere (only 417 ppm of which is associated with CO2), and that is not including the committed warming from the permafrost carbon feedback that would add another 0.1 to 0.2 °C this century (Macdougall et al, 2013).
Figure 1: Observed global warming (2010-2019 relative to 1850-1900) and the contribution to this net warming by observed changes to natural and anthropogenic radiative forcing. Reproduced from IPCC (2021).
Let’s once more explore the level of decarbonization required to keep warming below 2°C (recognizing that 1.5°C is no longer attainable). I present results from the UVic Earth System Climate model discussed in Weaver et al. (2007) and my book Keeping our Cool: Canada in a Warming World.
Starting from a pre-industrial equilibrium climate, I force the UVic model with observed natural and human-caused radiative forcing until the end of 2005. After 2005, future trajectories in emissions must be specified. Each of the post-2005 scenarios I use assumes that contributions to radiative forcing from sulphate aerosols and greenhouse gases other than carbon dioxide remained fixed throughout the simulations. An alternative way of looking at this is that any increase in human- produced, non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gases is assumed to be balanced by an increase in sulphate aerosols (or some other negative radiative forcing). This assumption should be viewed as extremely conservative, since most future emissions scenarios have decreasing sulphate emissions and increasing emissions of non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gases.
We’ll start by examining the effects of a hypothetical international policy option that linearly cuts emissions by some percentage of 2006 levels by 2050, and maintains emissions constant thereafter until the year 2500 (see Figure 2a). Of course, my baseline case of constant 2006 emissions is substantially more optimistic than the IPCC scenarios, some of which have 2050 emissions at more than double 2006 levels. The various pathways in emissions lead to atmospheric carbon dioxide levels in 2050 ranging from 407 ppm to 466 ppm, corresponding to warming relative to 1800 of between 1.5°C and 1.8°C (Figure 2b and Figure 2c). As the twenty-first century progresses, the atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and warming begin to diverge between scenarios, and by 2100 the range is 394 ppm to 570 ppm (we are presently at 417 ppm), with a warming of between 1.5°C and 2.6°C. None of the emissions trajectories lead to an equilibrium climate and carbon cycle in 2500, although the 90% and 100% sustained 2050 emissions reductions have atmospheric carbon dioxide levels that are levelling off. Of particular note is that by 2500, the scenario depicting a 100% reduction in emissions leads to an atmospheric carbon dioxide level below that in 2006, although global mean surface air temperature is still 0.5°C warmer than in 2006 (1.5°C warmer than 1800). While this version of the UVic Earth System Model only calculates the thermal expansion component of seal level rise and ignores contributions from glacier and ice sheet melt, the results shown in Figure 2d indicate that sea level rise still has not equilibrated even after 500 years. 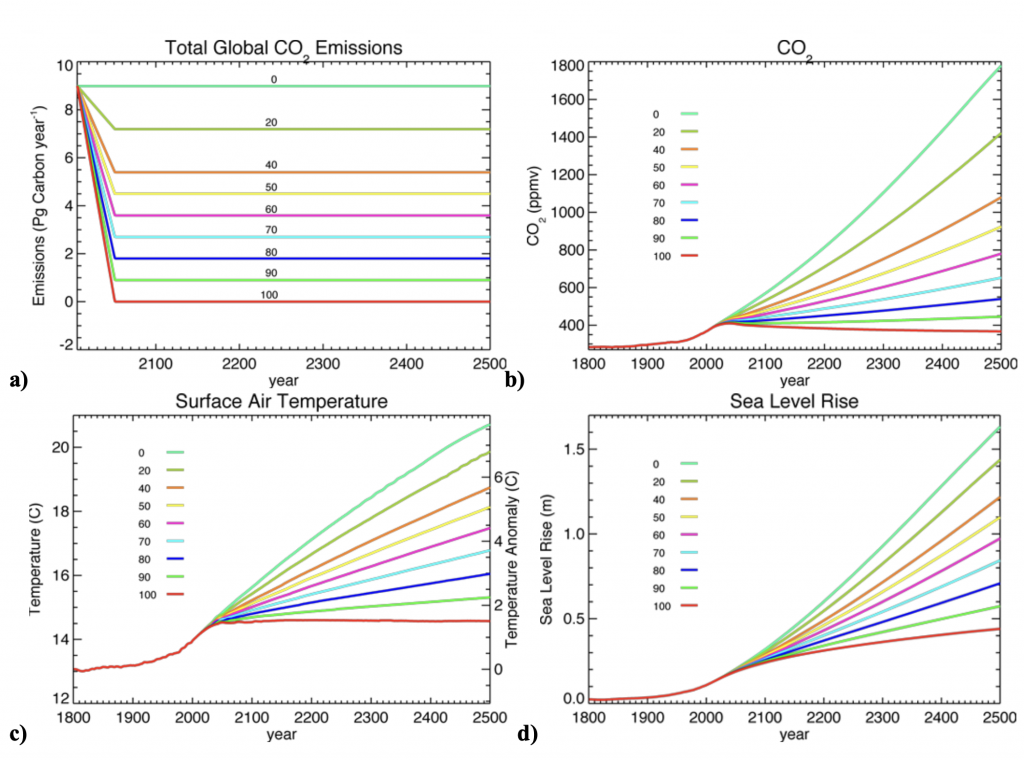 Figure 2: (a) Observed anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions from 1800 to 2006 (red) followed by linear reductions of 0–100% of 2006 levels by 2050. From 2050 onwards emissions are held constant. Transient evolution of globally-averaged (b) atmospheric carbon dioxide, (c) surface air temperature, and (d) sea level rise due to thermal expansion for all experiments. Note that the sea-level curves have no contribution from the melting of land-based ice.
Figure 2: (a) Observed anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions from 1800 to 2006 (red) followed by linear reductions of 0–100% of 2006 levels by 2050. From 2050 onwards emissions are held constant. Transient evolution of globally-averaged (b) atmospheric carbon dioxide, (c) surface air temperature, and (d) sea level rise due to thermal expansion for all experiments. Note that the sea-level curves have no contribution from the melting of land-based ice.
All simulations that have less than a 60% reduction in global emissions by 2050 eventually break the threshold of 2°C warming this century. Even if emissions are eventually stabilized at 90% less than 2006 levels globally (1.1 billions of tonnes of carbon emitted per year), the 2°C threshold warming limit is eventually broken well before the year 2500. This implies that if a 2°C warming is to be avoided, direct CO2 capture from the air, together with subsequent sequestration, would eventually have to be introduced in addition to 90% reductions in global carbon emissions.
I purposely kept emissions constant after 2050 in my idealized scenarios to illustrate that cutting emissions by some prescribed amount by 2050 is in and of itself not sufficient to deal with the problem of global warming. Even if we maintain global carbon dioxide emissions at 90% below current levels, we eventually break the 2°C threshold. This is because the natural carbon dioxide removal processes can’t work fast enough to take up the emissions we emit to the atmosphere year after year. Any solution to global warming will ultimately require the world to move towards net zero emissions carbon which requires the introduction and global scale up of negative emission technology.
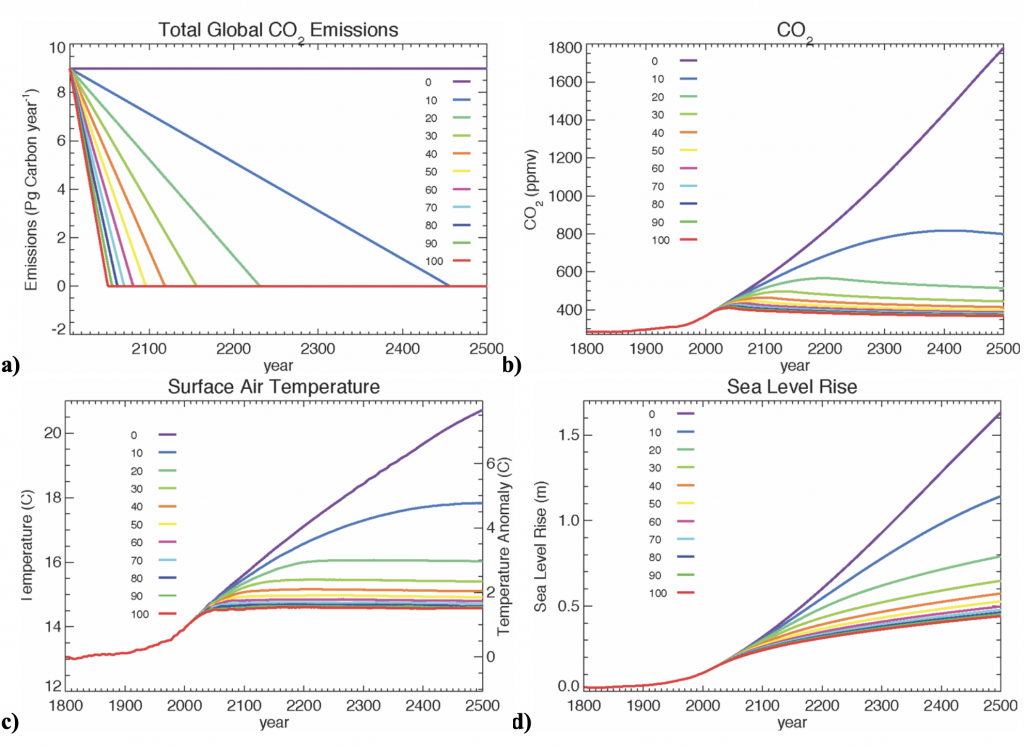
Figure 3: As in Figure 2 but the emissions in (a) continue the linear decrease until zero emissions are reached. The year in which zero emissions is reached is indicated in the table below.
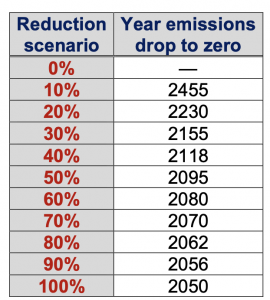 Now let’s examine the effects of another hypothetical international policy option that starts from the results obtained in the previous suite of experiments at 2050 but now continues to linearly decrease emissions at the same rate until zero emissions are reached. The resulting emissions are shown in Figure 3a and the date at which emissions fall to zero is given in table to the right.
Now let’s examine the effects of another hypothetical international policy option that starts from the results obtained in the previous suite of experiments at 2050 but now continues to linearly decrease emissions at the same rate until zero emissions are reached. The resulting emissions are shown in Figure 3a and the date at which emissions fall to zero is given in table to the right.
If we keep emissions on a linearly decreasing emissions path to carbon neutrality, it turns out that in the UVic model about 45% or larger reductions (relative to 2005 levels) are required by 2050 if we do not wish to break the 2°C threshold. And peak atmospheric carbon dioxide levels reach a little over 450 ppm before settling down to slightly above 400 ppm. Notice that in all cases, even though emissions have gone to zero, sea level continues to rise. It’s further important to note that these simulations were conducted and published in 2007 and assumed the hypothetical scenario of an immediate curtailing of emissions. The reality is global fossil carbon emissions (excluding land use emissions) were 10.1 GtC (billions of tonnes of carbon) in 2021 which is a 25% increase from 2005 levels (when they were 8.1GtC).
In this section I have tried to emphasize that the only means of stabilizing the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is for humanity to achieve net zero carbon emissions. While the implementation of nature-based solutions provides some additional time before net zero must be reached to avoid breaking the 2°C guardrail, there is a danger that such efforts are being overly promoted by governments and industry to allow them to maintain the status quo of oil, gas and coal exploration and combustion.
It’s a question of timescale
 Millions of years ago when the atmosphere had much higher concentrations of carbon dioxide, trees, ferns, and other plants were abundant. These plants used the sun’s energy, together with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water, to create glucose or sugar and release oxygen back to the atmosphere (photosynthesis). As the years went by, plants would grow and die, and some of these dead trees and other vegetation would fall into swampy waters depleted in oxygen. In this environment, the organic matter only partially decayed and so turned into peat, a precursor for coal formation. Over time, shallow seas covered some of the swampy regions, depositing layers of mud or silt. As the pressure started to increase, the peat was transformed, over millions of years, into brown coal, then soft coal, and finally hard coal.
Millions of years ago when the atmosphere had much higher concentrations of carbon dioxide, trees, ferns, and other plants were abundant. These plants used the sun’s energy, together with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water, to create glucose or sugar and release oxygen back to the atmosphere (photosynthesis). As the years went by, plants would grow and die, and some of these dead trees and other vegetation would fall into swampy waters depleted in oxygen. In this environment, the organic matter only partially decayed and so turned into peat, a precursor for coal formation. Over time, shallow seas covered some of the swampy regions, depositing layers of mud or silt. As the pressure started to increase, the peat was transformed, over millions of years, into brown coal, then soft coal, and finally hard coal.
A similar process occurred within shallow seas where ocean plants (e.g., phytoplankton) and marine creatures would die and sink to the bottom to be buried in the sediments below. Over millions of years, the sediments hardened to produce sedimentary rocks, and the resulting high pressures and temperatures caused the organic matter to transform slowly into oil or natural gas. The great oil and natural gas reserves of today formed in these ancient sedimentary basins.
Today when we burn a fossil fuel, we are harvesting the sun’s energy stored from millions of years ago. In the process, we are also releasing the carbon dioxide that had been drawn out of that ancient atmosphere (which had much higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere than today). So, unless we can actually figure out a way to speed up the millions of years required to sequester carbon from the atmosphere and to convert dead plants back into peat and then coal (or oil and gas) the idea that we can somehow stop global warming solely through nature-based solutions isn’t realistic.
Nevertheless, and I reiterate, there are many positive reasons for planting new forests (afforestation), replanting old forests (reforestation), or reducing the destruction of existing forests (deforestation), including the restoration of natural habitat and the prevention of loss of biodiversity. However, trees only store carbon over the course of their lifetime. When these trees die, or if they burn, the carbon is released back to the atmosphere.
The danger of over reliance on nature based solutions
While nature-based solutions have an important role to play in climate change adaptation and the preservation of biodiversity, there is a growing danger that governments, industry and the general public will come to rely on them as a means to maintain the status quo.
Let’s take British Columbia’s LNG experience as an example.
 In the lead up the the 2013 provincial election I repeatedly pointed out the economic and environmental folly of somehow believing that BC would build prosperity through liquifying natural gas and shipping it to Asia. In fact, I quantified my concerns in one of the first blog posts I wrote in the BC Legislature. British Columbia residents were being told that at least five major LNG facilities would be built in BC by 2020. Today we have none, so I would suggest that my concerns about the economics of LNG were spot on.
In the lead up the the 2013 provincial election I repeatedly pointed out the economic and environmental folly of somehow believing that BC would build prosperity through liquifying natural gas and shipping it to Asia. In fact, I quantified my concerns in one of the first blog posts I wrote in the BC Legislature. British Columbia residents were being told that at least five major LNG facilities would be built in BC by 2020. Today we have none, so I would suggest that my concerns about the economics of LNG were spot on.
In 2018, when it was clear that BC’s plans for LNG were not going to materialize, the BC NDP picked up where the BC Liberals left off and further sweetened the tax credit regime for LNG Canada, the one remaining major LNG company left in BC. It was clear to me that British Columbia could not meet its legislated greenhouse gas reduction targets if the LNG Canada project was ever built and I wrote a detailed blog post pointing out that it was time for both the BC NDP and the BC Liberals to level with British Columbians about LNG. The BC NDP government remained adamant that BC could still reduce emissions to 40% below 2007 levels by 2030. I remained skeptical and feared that this target can only be achieved through creative carbon accounting and appealing to “nature-based solutions”. I believe I was and remain correct. The analysis above and my earlier blog posts should make that obvious. And nobody should be surprised to see Shell Canada now promoting its efforts to ensure “the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems such as forests, grasslands and wetlands” as a central component to its greenhouse gas mitigation strategy. Of course, there is no mention of greenhouse gas emissions from the ever increasing area burnt by Canadian wildfires, nor the emissions being triggered as permafrost thaws and the previously frozen organic matter begins to decompose.
The Darkwoods Forest Carbon project offers a glimpse into what is likely being considered by BC government and industry decision-makers as a means of offsetting emissions from the natural gas sector. The problem with this is threefold.
First, claiming that the preservation of a forest should be considered a carbon offset using an argument that the wood would otherwise be harvested is a bit like me say to you: “give me $10,000 or I will buy a gas-guzzling SUV”! Second, if you want to claim a carbon credit for planting a tree, then you have to also accept a debit if that tree, or another, burns down. Third, there is no international mechanism to get credit for such a nature-based offset and these are purely considered voluntary.
Summary
In this post I have tried to outline the important role that nature-based climate solutions play amid the suite of policy options available to government and industry. The cautionary tale is that while these represent important contributions to a jurisdiction’s overall climate change adaptation and mitigation strategy, they cannot take away from the requirement to decarbonize energy systems immediately. As outlined in a recent article published in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B by researchers from Oxford University in the UK, “there are concerns over their reliability and cost-effectiveness compared to engineered alternatives, and their resilience to climate change.”
For years I have noted that the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2015 had immediate consequences for oil, gas and coal exploration. At the time of its signing, and given the availability of existing technologies, the Paris Agreement translated to the notion that effective immediately, no new oil, gas or coal infrastructure could be built anywhere in the world if we want to keep warming to below 2°C. This follows since such major capital investments have a long payback time; you don’t build a natural gas electricity plant today only to tear it down tomorrow. Socioeconomic inertia in the built environment also suggests that the capital stock turnover time would be decades, not years.
 Nature based-solutions are really a natural branch of other so-called Carbon Dioxide Removal geoengineering projects. Another solution that has received some attention of late concerns increasing the alkalinity of surface waters through dissolution of limestone. This geo-engineering fix was one of many examined by the IPCC in a 2005 special report assessing the possibility of capturing and storing carbon dioxide. To sequester 1 kilogram of carbon dioxide without the negative effects associated with acidification 3.5 kilograms of calcium carbonate (limestone) would have to be artificially dissolved in the ocean. Today, about 6.6 Gt of limestone is mined annually. If the entirety of this global production was dissolved in the ocean, about 1.9 Gt of carbon dioxide could be sequestered annually (or 0.5 Gt of carbon equivalent). This represents about 5% of the world’s 2021 global carbon dioxide emissions. A twenty-fold increase in limestone mining to sequester our present-day emissions would have enormous energy implications (with their concomitant emissions), not to mention the potential environmental impacts of such expanded mining activities. We would also have to stop producing cement, which uses this limestone, throughout the world, meaning that concrete could no longer be used in construction. It should be clear that attempting to modify surface alkalinity using the world’s limestone resources is not a serious proposition to combat global warming.
Nature based-solutions are really a natural branch of other so-called Carbon Dioxide Removal geoengineering projects. Another solution that has received some attention of late concerns increasing the alkalinity of surface waters through dissolution of limestone. This geo-engineering fix was one of many examined by the IPCC in a 2005 special report assessing the possibility of capturing and storing carbon dioxide. To sequester 1 kilogram of carbon dioxide without the negative effects associated with acidification 3.5 kilograms of calcium carbonate (limestone) would have to be artificially dissolved in the ocean. Today, about 6.6 Gt of limestone is mined annually. If the entirety of this global production was dissolved in the ocean, about 1.9 Gt of carbon dioxide could be sequestered annually (or 0.5 Gt of carbon equivalent). This represents about 5% of the world’s 2021 global carbon dioxide emissions. A twenty-fold increase in limestone mining to sequester our present-day emissions would have enormous energy implications (with their concomitant emissions), not to mention the potential environmental impacts of such expanded mining activities. We would also have to stop producing cement, which uses this limestone, throughout the world, meaning that concrete could no longer be used in construction. It should be clear that attempting to modify surface alkalinity using the world’s limestone resources is not a serious proposition to combat global warming.
So in summary, despite the many benefits of nature-based solutions, what is required to keep global warming to below 2°C (or, frankly, to stabilize it at any level), is the immediate transition towards the decardonization of global energy systems along with the widespread introduction of negative emission technology, such as direct air carbon capture and deep underground storage. At this stage, I am of the belief that this remains the only hope humanity has for a long term solution to this problem. We can take comfort in the very real successes of nature-based solutions, and their many co-benefits, but we cannot take our eyes off the scale of the challenge before us. Fortunately, all the solutions are known. It is a matter of individual, institutional, corporate and political will as to whether or not we will achieve the goals of net zero emissions in the future.
Unfortunately BC Greens force baby to get thrown out with bathwater on Clean Energy Bill
Last week I wrote about BC NDP’s Bill 17: Clean Energy Amendment Act, 2020 that proposed amendments to the Clean Energy Act allowing BC Hydro to:
- Implement a 100% clean energy standard;
- Remove BC Hydro’s self-sufficiency provision. That is BC Hydro is currently required to hold the rights to enough electricity from generating facilities solely within the province to meet its projected energy demand (more on this below).
- Remove Burrard Thermal from the list of heritage assets which would allow BC Hydro to dispose of, or develop, this asset.
In my blog post entitled Bill 17, Burrard Thermal, BC Hydro self sufficiency and clean electricity, I detailed a series of amendments that ensured:
- BC can still implement a 100% clean energy standard;
- Burrard Thermal will be removed from the list of BC Hydro’s heritage assets;
- BC Hydro’s self sufficiency requirement for average water conditions at their legacy hydro electric dams is retained;
- The definition of clean electricity reverts back to the original Clean Energy Act.
That blog post, together with my exchange during Question Period with the Minister of Energy Mines and Petroleum Resources on July 15th, provides a comprehensive analysis of why I proposed the amendments. I conclude the post with this:
I have communicated my intention of supporting the bill at second reading to both the BC NDP and the BC Liberals. If the bill fails at second reading, I won’t get a chance to introduce my amendments during committee stage and I fear that its positive aspects will be lost. That is, the preverbial baby will be thrown out with the backwater. The onus is ultimately on my former colleagues in the BC Green Party to indicate whether or not they support the Bill as it stands, or the amended Bill as I have proposed. Under the “good faith and no surprises clause” of the Confidence and Supply Agreement Premier Horgan and I signed in 2017, the BC Greens will have to communicate their intentions to government prior to the bill being called for debate.
In an odd press release and through an an even more odd, and unsupportable amendment, the BC Greens made it clear that this Bill will die on the order papers. And this troubles me.
The press release appears to be tone deaf. The feedback my office received from Indigenous communities has been almost exclusively on the government’s proposed removal of the self sufficiency clause (see my blog and also my Question Period exchange for more details). Yet the BC Greens propose no amendments in this regard and instead make the bizarre claim that more consultation is needed. The BC Greens could have either proposed to support my amendments to remove the self sufficiency clause, which has been sitting on the order papers since July 14, or introduced similar amendments themselves. This would ensure that the very positive aspects of Bill 17 are passed in a timely fashion. They chose not to, thereby ensuring Bill 17 will die on the order papers.
Unfortunately, the BC Greens’ proposed amendment is unsupportable and in my view shows a lack of understanding of the complexities of the energy file. I too heard feedback from stakeholders that the definition of clean electricity was problematic. However, many of the people raising this issue didn’t realize that the existing Clean Energy Act has very similar regulation enabling legislation. My amendments ensured that the existing definition remained in place for clarity.
Below I reproduce all definitions so I can expand upon this:
The various definitions
1) Existing definition in Clean Energy Act:
“clean or renewable resource” means biomass, biogas, geothermal heat, hydro, solar, ocean, wind or any other prescribed resource;
[there is no definition of clean electricity]
2) BC NDP government proposed change:
“clean electricity” means electricity
(a) generated from a clean resource, or
(b) deemed under the regulations to be clean electricity;
“clean resource” means a prescribed resource;
3) My proposed amendment to government’s change:
“clean electricity” means electricity generated from a clean or renewable resource;
(a) generated from a clean resource, or
(b) deemed under the regulations to be clean electricity;
“clean resource” means a prescribed resource;
4) BC Green proposed amendment to government’s change:
“clean electricity” means electricity generated from a renewable non-fossilized resource, including biomass, biogas, geothermal heat, hydro, solar, ocean and wind;
(a) generated from a clean resource, or
(b) deemed under the regulations to be clean electricity;
“clean resource” means a prescribed resource;
You’ll see that the government proposed to essentially leave the definition of “clean electricity” up to regulation. My amendments simply reverted the definition to what has been in place in the existing Act for more than a decade.
The BC Greens basically took the existing definition in the Clean Energy Act and added “non fossilized resource”. While at first glance this might seem sensible, it is problematic for a number of reasons:
1) “non-fossilized resource” is not defined in the bill.
2) Their definition of “clean electricity” may in fact preclude aspects of the establishment of a hydrogen economy. One of the main ways to generate hydrogen is to use steam-methane reformation and partial oxidation to strip it from methane molecules.
3) Despite the BC Green claim, leaving in: “clean resource” means a prescribed resource means that the definition of clean electricity and clean resources is not in fact stronger. It is, ironically, weaker.
In summary, it appears to me that rather than doing what is right and ensuring that the key aspects of the bill are retained while more work is done on the self sufficiency clause, as I proposed, the BC Greens have chosen to introduce 11th hour politically-motivated amendments as a face-saving exercise.
I am profoundly disappointed in the BC Greens for forcing the baby to be thrown out with the bathwater on Bill 17. As I noted earlier, under the “good faith and no surprises clause” of the Confidence and Supply Agreement Premier Horgan and I signed in 2017, the BC Greens should communicate their intentions to government prior to the bill being called for debate. I’m not sure what the BC Greens were thinking, but I certainly understand why the BC NDP might not choose not to bring this bill forward for debate in light of the uncertainty created by the BC Green position on this file.
Bill 17, Burrard Thermal, BC Hydro self sufficiency & clean electricity
Over the last few days there has been a flurry of emails to MLAs around the province concerning BC NDP’s Bill 17: Clean Energy Amendment Act, 2020. These emails articulate opposition to the removal of BC Hydro’s “self sufficiency clause”.
Let’s take a look at this issue in more detail.
Bill 17 proposes changes to the Clean Energy Act and Utilities Commission Act to give BC Hydro the ability to consider a range of energy resources and asset options as it prepares its Integrated Resource Plan.
The bill has been put together in what teachers reading this will recognize as a “two stars and a wish” format. That is, sandwiched between two very positive changes is one that is creating a great deal of concern.
The bill proposes amendments that will allow BC Hydro to:
- implement a 100% clean energy standard;
- Remove BC Hydro’s self-sufficiency provision. That is BC Hydro is currently required to hold the rights to enough electricity from generating facilities solely within the province to meet its projected energy demand (more on this below).
- Remove Burrard Thermal from the list of heritage assets which would allow BC Hydro to dispose of, or develop, this asset.
You’ll get absolutely no argument from me about the importance of implementing a 100% clean energy standard. The bill does not require 100% of BC’s electricity to be produced from clean sources, but it does set up a reporting structure and the intention is clearly to move in that direction as part of CleanBC, which the BC NDP government and I developed collaboratively in 2018. The requirement for 100% clean electricity would have to be set through regulation (Order in Council) and presumably that would occur after consultation with Washington, Oregon and California as to the precise definition of what is considered “clean electricity”. Presently, about 95% of BC’s electricity is generated from renewables.
You’ll also get absolutely no argument from me about the needs to mothball Burrard Thermal. Burrard Thermal was shut down in 2016 by the previous BC Liberal government after announcing it would do so in 2013. It sits on 78 acres of waterfront property in Port Moody that could be put to better use. What’s particularly strategic about the location is that it already has transmission lines to the area and so could supply power to heavy users of clean electricity. In fact, this strategic asset could be used as a carrot to attract to our province industry looking for access to clean energy as a means of demonstrating corporate leadership and developing green branding. Ever since I got elected in 2013, I have been pointing out that British Columbia should be using its abundant clean electricity resources to attract cleantech and manufacturing industries here. And so I am very supportive of government’s intentions in this regard.
What’s more troubling is the removal of BC Hydro’s self-sufficiency provision. In reality, BC Hydro does not actually have a stringent self-sufficiency clause in place, although we used to. That’s because on February 3, 2013 the BC Liberals relaxed this clause (to protect ratepayers from hydro increases) by changing the requirement for BC Hydro to be self sufficient for average instead of critical (i.e. the most adverse sequence of stream flows occurring within the historical record) water conditions at their legacy hydro electric dams. Back in May 2019, I expanded on BC Hydro’s lack of self sufficiency in a series of questions I asked the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources.
Much like the BC Liberals wanted to protect ratepayers from hydro increases, the BC NDP clearly want to do the same. The removal of the rest of the self sufficiency clause would create electricity trading opportunities with the United States via the highly successful power trading arm of BC Hydro — Powerex. The US is awash with very cheap solar power that Powerex could purchase during the day and at night, when the sun isn’t shining, they could sell back hydro power from our legacy dams at a premium. The arbitrage opportunities are boundless and it is no doubt that this would a) protect ratepayers from hydro rate increases and b) bring in much needed revenue to our province.
But here’s the twist, in doing so, we will likely put the final nail in the coffin for BC’s once vibrant clean energy sector.
When the BC NDP introduced Bill 17: Clean Energy Amendment Act, 2020 on June 23, I immediately determined that it was problematic. The problem was not with the desire for BC Hydro to keep rates low or use our legacy dams like batteries (one of my very first blog posts upon getting elected was on this topic), but rather that some of the unforeseen consequences and missed opportunities had not been fully explored (see for example my question to the Minister of Energy Mines and Petroleum Resources on July 15, 2020). And so I immediately set out to work with the BC Legislative drafters to propose amendments to the Bill (reproduced below). The amendments have been sitting on the order papers since July 14 and will be moved during committee stage for Bill 17.
The amendments ensure that:
- BC can still implement a 100% clean energy standard;
- Burrard Thermal will be removed from the list of BC Hydro’s heritage assets;
- BC Hydro’s self sufficiency requirement for average water conditions at their legacy hydro electric dams is retained;
- The definition of clean electricity reverts back to the original Clean Energy Act.
Should these amendments pass, the positive aspects of Bill 17 will be retained whereas the more troubling components will be removed.
I have communicated my intention of supporting the bill at second reading to both the BC NDP and the BC Liberals. If the bill fails at second reading, I won’t get a chance to introduce my amendments during committee stage and I fear that its positive aspects will be lost. That is, the preverbial baby will be thrown out with the backwater. The onus is ultimately on my former colleagues in the BC Green Party to indicate whether or not they support the Bill as it stands, or the amended Bill as I have proposed. Under the “good faith and no surprises clause” of the Confidence and Supply Agreement Premier Horgan and I signed in 2017, the BC Greens will have to communicate their intentions to government prior to the bill being called for debate.
I look forward to the exciting opportunities for innovation that present themselves with the removal of Burrard Thermal from the list of BC Hydro’s heritage assets and the move of BC to 100% clean electricity.
Proposed Amendments to Bill 17
17 Mr. Weaver to move, in Committee of the Whole on Bill (No. 17) intituled Clean Energy Amendment Act, 2020, to amend as follows:
SECTION 1, by deleting the text shown as struck out and adding the underlined text as shown:
1 Section 1 (1) of the Clean Energy Act, S.B.C. 2010, c. 22, is amended
(a) in the definition of “acquire” by striking out “used in relation to the authority” and substituting “in sections 7, 12 and 15”,
(b) by adding the following definitions:
“clean electricity” means electricity generated from a clean or renewable resource;
(a) generated from a clean resource, or
(b) deemed under the regulations to be clean electricity;
“clean resource” means a prescribed resource;
“compliance period” means a prescribed period; , and
(c) by repealing the-definition of “electricity self sufficiency”, and
(d)(c) by adding the following definitions:
“grid-connected customer” means a person in British Columbia who receives service through a direct or indirect connection to the British Columbia electrical transmission grid, other than a person in the Northern Rockies Regional Municipality;
“regulated person” means
(a) the authority,
(b) a prescribed public utility or class of public utilities, or
(c) a prescribed person or class of persons who deliver electricity to grid-connected customers; .
SECTION 2, by deleting the text shown as struck out and adding the underlined text as shown:
2 Section 2 is amended by adding the following paragraph:
(a) by repealing paragraphs (a) and (n), and
(b) by adding the following paragraph:
(q) to serve grid-connected customers with clean electricity.
SECTION 3, by deleting section 3.
SECTION 4, by deleting section 4.
SECTION 6, by deleting section 6.
SECTION 8, by deleting the text shown as struck out and adding the underlined text as shown:
8 Section 37 is amended by adding the following paragraphs:
(a) by adding the following paragraphs:
(a.1) for the purposes of the definition of “clean electricity” in section 1 (1), deeming electricity delivered under any of the following to be clean electricity:
(i) a specified contract or class of contracts;
(ii) a specified rate or class of rates;
(iii) a specified international agreement;
(a.2) a regulation made under paragraph (a.l) may prescribe that of the electricity delivered, a specified percentage is deemed to be clean electricity;
(a.3) prescribing resources for the purposes of the definition of “clean resource” in section 1 (1);
(a.4)(a.1) prescribing a period for the purposes of the definition of “compliance period” in section 1 (1);
(a.5)(a.2) prescribing public utilities, classes of public utilities, persons and classes of persons for the purposes of the definition of “regulated person” in section 1 (l); ,
(b) in paragraph (c) by striking out “sections 6 and 13” and substituting “section 13”, and
(c) by adding the following paragraphs:
(j) prescribing requirements for the purposes of section 19.1;
(k) prescribing matters that must be addressed in a report prepared under section 19.2 (1);
(l) for the purposes of section 19.2 (2), prescribing requirements respecting the preparation, verification and submission of reports, including, without limitation, the following:
(i) respecting the form and content of reports;
(ii) respecting who may conduct verifications;
(iii) respecting the conduct of verifications;
(iv) requiring reports or statements in relation to verifications, and respecting the form and content of those reports and statements;
(v) respecting the dates by which reports must be submitted to the minister.
SECTION 10, by deleting section 10.
SECTION 11, by adding the underlined text as shown:
11 Sections 44.1 (8) (b), 44.2 (5) (c), 46 (3.1) (c) and 71 (2.1) (c) and (2.5) (c) of the Utilities Commission Act, R.S.B.C. 1996, c. 473, are amended by striking out “sections 6 and 19 of the Clean Energy Act” and substituting “sections 6, 19 and 19.1 of the Clean Energy Act”.
On the clean energy economic opportunity for Indigenous communities in BC
Today in the legislature I rose during question period to ask the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources how he reconciles his government’s claim that it is committed to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples while at the same time introducing measures that will restrict their opportunities for clean energy economic development. I also asked him whether he was willing to instruct B.C. Hydro to declare force majeure on the existing Site C construction contracts, as opposed to the IPP contracts, to save billions upon billions of ratepayer dollars, and instead instruct B.C. Hydro to issue calls for power at market rate for any future power needs.
Below I reproduce the text of our exchange.
Video of Exchange
Question
A. Weaver: Many Indigenous communities in British Columbia anticipated being able to sell surplus electricity to B.C. Hydro. Despite this government’s professed commitment to reconciliation, the decision by B.C. Hydro to cancel its standing offer program has placed these communities in a very difficult position.
As I’m sure the minister is aware, reconciliation is a multifaceted process that involves building genuine, long-lasting economic partnerships with Indigenous communities. Otherwise many such communities will continue to struggle economically. More recently, with the proposed changes to the self-sufficiency clause in the Clean Energy Act, First Nations aspiring to become clean energy producers will be dealt yet another serious blow.
My question is to the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources. How can this government claim that it is committed to reconciliation with Indigenous peoples while at the same time introducing measures that will restrict their opportunities for economic development?
Answer
Hon. B. Ralston: I want to thank the member for Oak Bay–Gordon Head for his question. Let’s begin by remembering that the old government signed insider deals for power at five times the market price. That created a $16 billion obligation owed by British Columbians. That’s $16 billion in unnecessary costs.
We are committed to keeping B.C. Hydro rates low and building a low-carbon economy for people. Maintaining affordable electricity is critical to electrifying our economy and meeting our CleanBC goals. The standing offer program was not compatible with this.
Our government understands — and I acknowledge the import of the member’s question — that many Indigenous communities view small-scale private power as economic development opportunities. Indeed, when we suspended the standing offer program in February 2019, we exempted five projects in development that had significant First Nations involvement.
I agree with the member that it’s important to support Indigenous communities in clean energy economic development. Just last month we announced $13 million for four clean energy projects to help remote communities get off diesel.
Supplementary Question
A. Weaver: Over the last decade, numerous First Nations have banked heavily on clean energy projects as an economic development strategy. Many have entered into agreements with independent power producers to do the same. On Vancouver Island, for example, 13 of the 14 Nuu-chah-nulth First Nations are either current or perspective stakeholders in renewable energy products. The Tla-o-qui-aht Nation has poured over $50 million into clean energy projects and has plans to spend an additional $100 million.
Successful endeavours, such as the T’Sou-ke Nation’s solar farm in the Premier’s own riding, have helped get Indigenous nations off diesel, while others that have received financial backing from the government promise to do the same. For many Indigenous communities across British Columbia, the opportunity to sell excess electricity is a vital component of their future economic plans.
My question, once more, is to the Minister of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources. Will the minister instruct B.C. Hydro to declare force majeure on the existing Site C construction contracts, as opposed to the IPP contracts, to save billions upon billions of ratepayer dollars, and instead instruct B.C. Hydro to issue calls for power at market rate for any future power needs?
To remind the minister, market rate is not 20 cents a kilowatt hour. It’s not 15 cents a kilowatt hour. It is a few cents a kilowatt, as is demonstrated worldwide with the price of solar and wind being lower than the price of coal and natural gas combustion in most jurisdictions.
Answer
Hon. B. Ralston: Once again, I’d like to thank the member for Oak Bay–Gordon Head for his question. As a government, we are committed to working collaboratively with Indigenous communities on opportunities for economic development. We consulted widely, including engagement with Indigenous nations, on the Comprehensive Review of B.C. Hydro: Phase 2 Interim Report, which includes the proposal on the self-sufficiency requirement.
I think it’s important to note that the changes that we are proposing will not happen overnight. They will allow B.C. Hydro to consider out-of-province energy, as one option — one option among many — to providing clean and affordable energy, as part of their next 20-year plan. These changes support our climate plan, CleanBC, and they allow B.C. Hydro to continue purchasing power from First Nations-owned projects.
My ministry has a wide range of programs that support Indigenous communities to transition to clean energy and improve energy efficiency. For example, we’ve invested $5 million in the B.C. Indigenous clean energy initiative. This initiative supports community clean energy projects. I appreciate the member’s questions on this important topic. Our government will continue to work with Indigenous communities to identify clean energy opportunities.