Environment
Auditor General’s report demonstrates it’s time to get serious on climate action plan
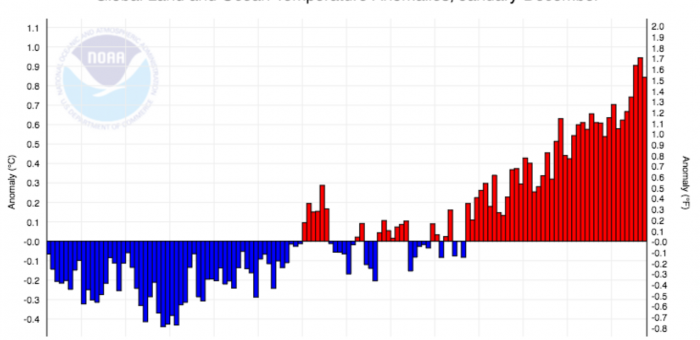
It’s been a busy day in the BC Legislature. Right after Question Period, the Speaker presented the Auditor General’s report entitled Managing Climate Change Risks.
Not surprisingly, the Auditor General concludes that “government is not adequately managing the risks posed by climate change” and that “government has not taken adequate action to meet provincial emission reduction targets”.
Below are my comments on the release of this welcome report.
Media Release
Weaver: Auditor General’s report demonstrates it’s time to get serious on climate action plan
For immediate release
February 15, 2018
VICTORIA, B.C. – Andrew Weaver, leader of the B.C. Green Party, released the following statement on the Auditor General’s report, Managing Climate Change Risks: An Independent Audit.
“The Auditor General’s finding that the government is not adequately managing the risks posed by climate change is extremely serious and deserve our immediate attention,” said Weaver.
“The unfortunate trend of politicians making grand statements about the importance of climate action and then doing nothing to meet our targets must end. In 2008 we were world leaders in climate action. The previous B.C. Liberal government not only failed to build on the Climate Action Plan, but dismantled the elements of the plan that were already in place. Now, the Auditor General has found that the government has done little to address the effects of climate change that are already underway.
“The risks of inaction to our province are enormous. Climate change has unique ramifications for each of B.C.’s precious ecosystems. We need to be honest with British Columbians: do our targets mean anything? If we truly care about the impacts of climate change on the next generation, we must follow our words with decisive action.
“Through our inaction we risk following behind greater global economic trends. In this minority government, we have an opportunity to make climate leadership a foundational accomplishment that drives our vision for the future of the province. We need a diversified, sustainable 21st century economy – one that will serve today’s generation without burdening generations to come. Other jurisdictions worldwide are reaping the economic rewards of the explosive growth in renewable energy. B.C. has everything we need to be a leader cleantech – just today it was announced that B.C. will receive a portion of federal supercluster funding. It’s time to stop chasing the sunset industries of yesterday and embrace these exciting opportunities.”
-30-
Media contact
Jillian Oliver, Press Secretary
+1 778-650-0597 | jillian.oliver@leg.bc.ca
Responding to the February 2018 Speech from the Throne
Today in the Legislature I rose to speak to the first BC NDP Speech from the Throne. As I noted in my brief media statement following the Throne Speech, I am encouraged to see our shared values represented in the speech.
Below I reproduce the text and video of my nearly two hour long response.
Text of Speech
A. Weaver: Please let me start by saying congratulating the new Leader of the Official Opposition, who just spoke to the throne speech a few minutes ago. I recognize that it’s a lot of work going through a leadership campaign, particularly one that was, frankly, quite interesting and quite well contested. So congratulations to the leader. I look forward to months and years of working collectively, particularly on this day, Valentine’s Day.
I’d like to start my response to the Speech from the Throne also thanking my family, my constituents and, particularly, the hard-working staff who I am blessed to be able to work with on a day-to-day basis.
Like the Leader of the Official Opposition, I wish to congratulate now publicly whoever wins the by-election today in Kelowna West, an interesting riding made up of both West Kelowna and Westbank Nation and large parts of downtown Kelowna.
You know, I spent ten days in Kelowna this last little while knocking on doors and getting to know the Kelowna residents and the issues there. One of my first tasks was to actually go to Ben Stewart’s office and say to him: “Good luck, Ben. We’re going to make you work for this one.” So I’m excited to see what actually happens today. We know that the turnout is low. For whatever happens, I’m sure everyone on both sides of this House will welcome the new MLA with open arms and look forward to working with him or her as well in the days ahead.
I found this throne speech to be quite refreshing. I used the words “cautiously optimistic” to describe my initial response to this. There’s a number of areas covered in the throne speech — many, many areas — some of which are gone into in detail, some of which are in less such detail.
There’s no question, in my view, that people are, front and centre, the focus of this throne speech. I did particularly applaud the throne speech commemorating the good work of David Barrett, who, frankly, is one of my heroes, a man who stood for principle when he ran for politics, a man who made decisions based on evidence. Sometimes they weren’t popular decisions. But the test of time is such that meant much of his legacy still remains with us today, whether it be the agricultural land reserve, whether it be quite a number of our environmental programs and positions here in British Columbia or whether it be our public auto insurance, which, admittedly, is under some financial stress as we speak.
The throne speech outlines a number of areas in terms of affordability and housing; child care; economic opportunity; services for people, including health care; education; public safety; infrastructure; mental health; and, of course, a section towards the end on climate change.
Now, hon. Speaker, as you will know, the results of the last election were such that there was no clear majority of MLAs in this House. As such, the B.C. Green caucus went into negotiations with both the Liberals and the NDP to see if we could come to an agreement that would allow for confidence in supply to be given in throne speech and budget measures while retaining our autonomy in terms of a minority, as opposed to a coalition, government.
The key issue that our agreement ultimately came down upon was the issue of climate change, an issue where we felt that ultimately, the previous government was not really willing to take the steps necessary to deliver on the promises made, both at the time and previously, by the government led by Gordon Campbell — a government that, as you know, hon. Speaker, I supported and worked with to try to develop policy measures that were systematically dismantled year after year once leadership changed at that level.
I didn’t think it’d be easy. The last election campaign was not an easy one to be a B.C. Green. It was very personal, a lot of very partisan attacks. I honestly didn’t think it would be possible that the B.C. Greens would be able to set up a confidence and supply agreement with the B.C. NDP. There it is, in all honesty. It was a personal campaign.
But ultimately, in sitting at that table in those days in the lead-up to our final decision, it became apparent to me and to my colleague Sonia, who was at the table, that both the Premier and the now Finance Minister were people that we felt we could relate to, people who we believed ultimately wanted to put the best interests of British Colombians front and centre in decision-making — not the backroom crowd but British Columbians.
Again, people watching the media in the lead-up to the actual agreement would notice that there was some public tension between the Leader of the Official Opposition and myself in terms of some disagreements that typically got amplified far beyond what they actually were. But in those discussions, it became very clear to me that the Premier cared. He was a person who cared about the best wishes of not just his constituents but all British Colombians. And ultimately it was clear to me that we were going to go into an agreement with the B.C. NDP. I haven’t regretted it that since that day. The proof has been in what has been delivered in our discussions, our deliberations and where we have come to today.
Now, I recognize there’s a lack of substance in some of these issues brought forward in the throne speech, and I’m the first one to call out the fact that there’s a lot of rhetoric and, at times, little substance in some key areas. But my experience, our experience, over these last six or seven months has been one of collaboration, of actually being listened to, of actually trying to do what’s right as opposed to what’s populist.
You know, we see it now in what’s going on in British Columbia, where a government essentially says, “You know what? We recognize that the product that is in a pipe, diluted bitumen….” There had never been an environmental assessment process when that product switched from synthetic crude, which used to be shipped, and where diluted bitumen started getting packed in with that. There was never any assessment, and even in the NEB process, there were clear recommendations that came out and conditions that had to be met — a number of which are British Columbia conditions.
So when the government says that it’s going to do what it must do, which is look out for the interests of British Colombians by trying to develop an understanding of the science of diluted bitumen, if spilled over our streams and lakes as this product comes across this province — simply doing what’s right — we get a knee-jerk response, not only a petty response, from Alberta. But it saddens me most the way that the B.C. Liberals are playing politics over this.
The Leader of the Official Opposition just said that British Columbia will be an embarrassing jurisdiction. British Columbia will never be an embarrassing jurisdiction. He argued that if we don’t cave in to the demands of Alberta, we will become an embarrassing jurisdiction. What sort of jurisdiction is embarrassing, when we are the most beautiful place in the world to live, where we have some of the best and brightest minds in the world come here because of the quality of life we can offer?
Our education system worldwide is second to none. Industry is thriving, and we’re a destination of choice for people all over the world. I’m not embarrassed about that. I’ll never be embarrassed about that. Frankly, I’m proud to say that we support the decision of the Environment Minister and the Premier in terms of doing what’s right, in terms of listening to the Royal Society of Canada expert panel report, the National Academy of Sciences in the United States expert panel report. The former says we don’t know what’s going to happen with a spill of diluted bitumen; the latter says we simply can’t clean it up.
The Premier wants to simply explore the science behind that to ensure that we are protected here in British Columbia, that our natural beauty and the risk that we’re taking is actually mitigated, that someone’s willing to clean up. The response we get is that this is petty, and British Columbia will be an embarrassing jurisdiction if we don’t cave. Shame on the Leader of the Official Opposition for that.
To actually have the audacity to claim that somehow Alberta is right to take it out on the B.C. wine industry just is mind-boggling. We should be united together in this Legislature — united together, standing up for the B.C. wine industry, telling all of Canada that it is not okay to put the rights of a multinational based in Texas and its shareholders against small business owners in the Okanagan. Putting small business owners, putting family business, protecting the rights of British Columbians — that’s what we were elected to do. We’re not elected to ensure profits are maximized in a multinational. We’re elected to ensure that externalities are internalized and that if there’s going to be a spill, there’s money there available to clean up that spill. But nobody talks about that.
Then just yesterday we heard Mr. Trudeau say that in fact it was a horse trade. All of this was really just a horse trade, because we wanted Notley to bring in her climate plan, and the only way we’d get her to do that was if we gave her something. But we’re not going to give her the Energy East, because the mayor of Montreal was quite upset, and there are an awful lot of Liberal seats in Quebec that we might lose, and who cares about B.C. anyway? Who cares about B.C.? There’s only a few Liberal seats, and we might gain as many in Alberta and Saskatchewan as we lose in B.C.
This is the way the decision was made. It was not made because of what’s in the best interests of Canada or British Columbians.
Again, I was the only MLA in this Legislature who participated in that NEB process. I participated in two different ways. I was qualified twice: first as an expert, with background in ocean physics, and second as an MLA representing an affected area. In both those cases, we examined these documents very, very carefully.
Now, while I know members opposite and the government was very, very free and easy with approving, did they actually know that the entire oil spill response in that process was predicated on the existence of calm conditions, with no waves, winds blowing offshore, if any, and 20 hours of sunlight? Now, there is not a latitude south of Tuktoyaktuk that has 20 hours of sunlight on any day of the year. So you would think, as a participant asking for a more realistic scenario, that I’d get a response. But no, the response I get is: “The NEB has enough information on which to make a decision.”
I could outline a litany of these. The model that was used for the ocean circulation in the region — do you know how that’s validated? How do you think a model was validated? Now, these are complex numerical models that have thousands of lines of code, that are essentially discretizing very complex physics. The way it was validated, was a guy fell off a B.C. ferry who drifted. The model said: kind of drifted the right way. You can’t make this stuff up.
The boundary conditions for the model were validated using tides. Well, you don’t need a complex model, looking at the mixing in the Strait of Juan de Fuca or Georgia Strait, talk about tides. Tides we’ve known about for decades. The model was incorrect. It was not the appropriate tool to be used.
It was not only me who said it. It was David Farmer — Royal Society of London, distinguished scholar, who was also at the Institute of Ocean Sciences. He said the same thing, as did others who participated.
I applaud government, and I’m glad that they’re actually standing up. I’m glad that today, just moments ago, the government announced it would take steps to promote B.C. wines. My very first response was to go out and buy three bottles of B.C. wine: one from Thornhill Creek, ironically and quite appropriately Canada’s first carbon-neutral winery; one somewhat humorously from Dirty Laundry, based in Summerland — you know, joking NDP Alberta and NDP B.C., I thought it was appropriate; and the third one from Mission Hill, of course symbolic of the race that was there.
That was my response. What was the B.C. Liberal response? It was blaming government. It wasn’t standing up for industry. And what’s worse…. In those ten days I spent in Kelowna, I consulted wine industry expert after wine industry expert after restaurateur.
Let me tell you: the wine industry in B.C. is very, very upset at the B.C. Liberals right now. I’ll tell you why.
Let me tell you, the wine industry in B.C. is very, very upset at the B.C. Liberals right now, and I’ll tell you why. Because despite my protestations sitting opposite, pointing out that I did not believe that those specialty wine licences would stand up to a NAFTA challenge, and despite my saying, “Don’t do this. I’m not sure you’ve got the appropriate legal advice,” government went ahead and created six new specialty wine store licences for grocery stores to sell wines in B.C.
We’re not talking about the 50 or 60 — I forget the number — that were grandfathered in prior to these trade agreements, that are owned by the wine institute. These are six new ones that the government decided to create. Well, we now have a WTO trade complaint launched by Australia against British Columbia wines because of these six. We have a NAFTA challenge launched by the U.S. over these six licences.
That’s the B.C. Liberal response. They have the gall and the audacity to say that we’re not protecting B.C. wine — as the government announces measures today to actually promote B.C. wine — yet their direct policy measurements have led to WTO and NAFTA challenges directly against B.C. on the international scene.
You know, you should take a look at your own house before you start throwing stones at other people’s houses, to be honest. And that’s what is so refreshing about this throne speech. I truly believe it steps back and makes us reflect upon what’s important in British Columbia.
I’m going to go through the throne speech and give credit to now members of the opposition for some of the ideas in it that clearly were put forward by them and that have been adopted by the B.C. NDP.
For example, when we talk about the actions of affordability. In the throne speech, the B.C. NDP outline the number of actions that have happened, one of which was to cut MSP premiums in half.
Now, we recognize the B.C. Liberals had already promised that. They’d already promised to do that. Again, this is an issue that we felt we could have done much more aggressively, and we campaigned on eliminating them through bringing it into a progressive health care premium much akin to what’s done in Ontario, but we recognize that this has been done. We applaud this, and we congratulate the B.C. Liberals on making sure this happened.
Another thing that happened in there is they talk about affordability measures with respect to the removal of tolls. Now I recognize that the B.C. NDP campaigned on this. I recognize the B.C. Liberals were a little more subtle in their campaigning, and, rather than eliminating the tolls, they were going to put a cap on, which, frankly, was a little more clever because it would not have allowed for the transfer of debt onto provincial debt to be taxpayer-supported.
But in the throne speech that happened this summer, the Liberals were also going to eliminate the tolls. So we really were standing alone in saying we don’t support it. We continue not to support it, but that’s the nature of a democracy. We don’t believe that’s correct, but we understand that it’s moving forward, and the B.C. NDP — and, frankly, the B.C. Liberals — will have to explain that to the voters.
We’ve told you why we don’t like it. We don’t like it because we think it’s fiscally irresponsible policy. It’s a form of vote-buying, in our view, and it actually transfers onto provincial debt — taxpayer-supported debt — $4.7 billion. It puts us in a position where we can’t deal with some of the things that we might otherwise do, like stop Site C, which honestly is something that I still don’t understand to this day, based on the fiscal outlook of what that’s going to cost.
Also, in the case of the Golden Ears and Mann bridges, outlined as a success to date, we know that that was not done in consultation with local mayors who opposed it. The concern over this is there is a discussion right now happening in Metro Vancouver on mobility pricing. Whether that comes to fruition or not is not the issue. The issue is, once you pull away tolls, it’s very difficult to put them on. And there are unforeseen consequences, like people who wanted to pay those tolls because they wanted to have access in a more timely fashion to the Vancouver region.
Another action on affordability that was highlighted: cutting student loan interest by 2.5 percent so that graduates can get out of debt more quickly on their path to a chosen career. Obviously, we wholeheartedly support that. Again, this is something that the B.C. Liberals had promised to do.
I’m pleased that we have an example where the B.C. NDP have adopted something the B.C. Liberals have done that we agreed to as well. Let’s focus on our successes. We have all agreement in the House that this is a good thing to do. That’s what we’re elected to do — to put forward good public policy.
We hear about making adult education and language learning tuition-free, so that tens of thousands of British Columbians can prepare for a degree and upgrade their skills, work. Great public policy, something we supported — glad to see that that’s a success — and something that we started to see emerge in the Liberals’ throne speech in the summer as well.
On the topics of affordability in the throne speech, the government points to its attempt to keep hydro rates affordable. They’ve asked B.C.’s commission to freeze hydro rates for the next year.
Now, I appreciate the softening in that language, because obviously, you cannot have your cake and eat it too in this area, in light of the fact that you cannot campaign on freezing B.C. Hydro rates and also campaign on the autonomy of the BCUC, because they’re mutually inconsistent. Either you agree to the autonomy of the BCUC and make a suggestion that you’d like to see it frozen, or you freeze it through order-in-council, which, historically, had been done by the B.C. Liberals.
The reality is I’m not sure BCUC will approve that. Frankly, B.C. Hydro looks pretty foolish, after having a 4 percent increase approved by the BCUC as part of a long-term plan. They look pretty foolish going to the BCUC now and saying: “We don’t really want an increase.” If I were on the BCUC, I’d be asking: “So what’s changed with your accounting?” Frankly, it does not instill confidence in B.C. Hydro if they can actually suddenly justify, through different accounting, the lack of an increase.
You know, if BCUC rejects a freeze, so be it. I think the electorate are the ones who the government have to be accountable to. We did not campaign on freezing B.C. Hydro rates, nor did the B.C. Liberals, because frankly, I don’t think it’s fiscally responsible. And honestly, it doesn’t actually deal with the issue of affordability.
Let’s take a look at a simply example that would. Right now we have tier 1 and tier 2 rates. Now, if there were six people living in a small house, they are almost certainly going to be having six showers. They’re going to have six bedrooms that are heated. They might have an electric car that they share. But their fixed tier 1 rate is the same as somebody in a 10,000-foot mansion with one person.
The electricity usage is not normalized by the number of people it’s being applied to. It’s basically tier 1 based on your actual meter. That’s not right. That doesn’t actually address the issue. The issue would be addressed with by dealing with the rates — the rate of that tier 1, tier 2 — and focusing on providing assistance, like as has been done in other provinces, particularly in cold provinces where heating bills can be outrageous in the winter.
I’m getting a $750 electricity bill. It’s kind of high for two months, but there are four people in my house. I don’t know how somebody on a low income could afford 750 bucks, particularly if they live in Dawson Creek, particularly if they’re heating their homes with electricity instead of gas. How could they afford this?
These are the measures and means and ways we deal with the affordability issue, by targeting those who need the leg up, rather than blanket hydro rate freezes for one and all.
Interjection.
A. Weaver: Well, again — I’m not — I’ve never been opposed to…. Natural gas right now is a premium for heating. It’s actually quite cheap. It’s $2 and change at Chetwynd, I understand — $2.50 or something like that. Really, really cheap. You’re basically losing money taking it out of the ground in northern B.C. But the way you make money…. The reason why Fort Nelson has dried up is because there are dry gas fields, obviously. But we’ve got the liquids in the Montney, which we can actually sell.
On this topic that was so astutely brought up by my friend from Peace River South, I met in Kelowna West a fellow in a coffee shop who had just left Fort Nelson. He’d sold his natural gas company. The reason why he left is he felt the long-term economics of natural gas is not good in light of the fact that there is a global oversupply.
What’s his focus? Where has he moved into? He’s moved into the petrochemical and value-added industry in the carbon sector. There is a future. We are going to need plastics. We can actually extract hydrogen from the methane. We can actually create hydrogen, which a storage fuel. There is a lot of innovation potential that can and will happen in our natural gas sector, but it means we have to think differently from what we are doing.
In the throne speech, another success that was mentioned was ICBC. Or rather, the throne speech states: “Years of apparent neglect and inaction have led to big problems at B.C.’s public auto insurer. This government has rejected the double-digit increase in rates for drivers and has taken decisive action to keep rates down.” That’s a success outlined in response to the escalating financial crisis in ICBC.
Again, we were somewhat critical of government when, after the initial report was made public, things were taken off the table prior to standing back and reflecting upon that which was actually contained and what the solutions were, but we do support a number of the measures. We do believe that the red-light cameras being enabled is a good thing. They were just turned off. We do believe that we need to take a close look at some of the soft-tissue claims. We also like the focus where we’re focusing on the patient and the care rather than on the actual litigative aspects of ICBC.
There’s an awful lot that needs to be done. In other jurisdictions that have public insurance, there’s a form of no-fault. I know that trial lawyers will be very upset about this, but it’s a discussion we need to have, about keeping prices down. Other provinces that don’t have public insurance have a form of private insurance. With private insurance, you start to get rules and regulations as to why someone would actually offer you insurance, for example. They put limits on claims or they will limit the amount that they’ll pay off in claims. Again, we believe that that’s a discussion we should have.
Obviously, our preference is to fix ICBC. As I said at the very beginning, it is a legacy — frankly, a good legacy — of Dave Barrett, who was mentioned in the beginning of the throne speech as a leader in British Columbia. We continue to look forward to see how the Attorney General, who I see has joined us here…. I do apologize, hon. Speaker; I’m not supposed to mention about the presence or absence of any member in the House. We do look forward to seeing the measures that he will continue to outline as we move forward with respect to revitalizing ICBC.
To the issue of housing. We know that the issue of affordability is fundamentally coupled with the issue of housing availability and affordability. It’s not only reducing tolls. It’s not only eliminating MSP or reducing them. It’s actually being able to find a place to live and a house to live in that you can afford. Now, the B.C. NDP, during the last election campaign, campaigned vigorously on the fact that they would take be taking steps to deal with both supply and demand. I tend to agree with the Leader of the Official Opposition that the 114,000-new-unit number is wishful. I’m not so sure I understand where that number comes from, and I do resonate with the analysis that was presented.
On the other hand, I do recall — and I commend it, and continue to — the good work of the now Attorney General who was raising so many issues with respect to the demand side. We see, mentioned in the throne speech: “Government’s first step must be to address demand and stabilize B.C.’s out-of-control real estate and rental market.”
I’m very pleased to see those words there. We know that this is not a supply problem. It is a demand problem. We know that there are 7½ billion people in the world. We know that around the world there are tumultuous times. We know that real estate is a safe haven, particularly when it’s British Columbia real estate. A lot of capital is coming into B.C. That capital is being parked here as an investment, as a bank account to ensure that money is protected because of our stable democracy, our quality of life, our attractiveness and the fact that real estate, particularly in some regions, was affordable.
Hon. Speaker, I will be designate on this particular speech.
The issue of affordability is not only a Metro Vancouver issue nowadays. Perceived value is not there, to the extent that it was, in Vancouver. But perceived value is there in Victoria, in Kelowna, in Nanaimo, in Parksville and many other places in British Columbia where we’re now seeing prices dramatically increased as people leave Vancouver and say: “I’ll sell my $300,000 bungalow, which I bought 15 years ago, for millions. Then I’ll come and drop a million bucks in Victoria — what’s that? — and I’ll pocket $2 million and do very well, as a retirement fund.”
The problem here is that the disparity between income and rent, as well as housing, has grown so much that we have a crisis. Crises require dramatic steps. Tinkering around the edges will not deal with the problem.
My own property assessment value, its paper increase, went up 25 percent in one year. All that tells me is we need a 25 percent correction in the market where I live, because that’s a completely artificial gain. It doesn’t reflect the value of my home. It reflects speculation in my part of the riding of Oak Bay–Gordon Head, which has seen out-of-control real estate prices.
We called for bold steps, mirroring what was done in New Zealand, mirroring what was done in Australia. Bold steps to say we have a crisis now, and when you have a crisis, you need to deal with this in a very, very firm way. We called for a ban on offshore capital being allowed to buy property and land in British Columbia.
The stories we got — whether it be the thousands of hectares in northern B.C. that were bought up by offshore corporations to grow hay that is bubble wrapped and shipped abroad, creating an externality of rising hay prices in the region and lack of availability. This isn’t right. We’ve heard stories about one constituent who came into my office — well two of them, actually — how they had two friends, or friends of friends, come here on a tourist visa, and each of these business people bought five houses and then got on a plane and went home, and those five houses lie vacant.
We’ve got story after story after story flooding our in-box. And let me tell you, I have never seen so much for support for an issue as I have seen for support to take immediate steps to clamp down on the ability of offshore capital to come into British Columbia to purchase our real estate.
A number of years ago — I think it’s three years ago now — after senior homes and the issue of MSP premiums and the affordability issue that was raised, I raise it in this House. We started a campaign, a petition campaign. We started a public relations campaign to gauge public support. I think it was overwhelming that people felt it was a regressive tax, and they wanted to see it dealt with in a progressive fashion. We received thousands and thousands of emails. Our petition had tens of thousands of names on it. But that pales in comparison as to the support for taking steps now.
The most outspoken, the most passionate people speaking out are actually first-generation immigrants to British Columbia. People who came to British Columbia, with their families in many cases, for a better life. They came to this country because of what we could offer in terms of opportunities — for jobs, for places to live and for the beautiful environment.
Now they see that their children are no longer afforded the same opportunities that they were. These are the people speaking out. These are the people who are begging government to take steps. So while I asked it again today in question period, I got the same answer that we must wait for the budget.
Let me tell government that there is pent-up anxiety here on this issue, and we hope that government delivers on its promises. We certainly hope that government delivers on its promises.
We were somewhat disappointed with the response that is being done with respect to Airbnb. We recognize that it was a good first step from a taxation point of view. But Airbnb got the best advertising they could possibly have wanted here in British Columbia.
Unless you couple that with an aggressive ability to allow municipalities to actually limit, to have business licences or to tax though vacancy rates across the province, this will do little other than incentivize a particular company, a winner. The government has in essence chosen a winner. What about vrbo, vacation rentals by owner, another organization? What about the people who list on Craigslist? It’s a dangerous precedent to set when you are picking winners and losers, particularly when we’re in a close to 0 percent vacancy rate.
The throne speech says that government will introduce legislation to crack down on tax fraud, tax evasion and money laundering in B.C.’s real estate market. We are very excited about that. We welcome that, and again we look forward to the details that will be outlined, hopefully, in the budget coming up next week.
Again in the throne speech, the budget talks about, “the government will begin to make the largest investment in affordable housing in B.C. history, including social housing, student housing, seniors housing, Indigenous housing and affordable rentals for middle-income families,” and so on, so forth.
We welcome investment in affordable housing, and we look forward to seeing what the specifics are in this regard. We were very concerned about some of the language emanating out with respect to how the rental agreements will be changed, because we must protect renters and the rights of renters. But we also must protect the rights of landlords, particularly those people who didn’t have any pension — those people who put real estate as the source of their pension. If we start to clamp down on their ability to make ends meet, we don’t actually deal with the problem of affordability. We create an additional problem.
The throne speech talks about enabling local governments to plan for affordable rental housing by zoning areas of their communities for that. Again, we’re excited to see that this is coming through. It’s been asked for by both UBCM as well as the city of Vancouver. One of the things we campaigned on, which we’re pleased to see in there, is that the government plans, through the throne speech, to work with local governments to help plan for and build housing near transit corridors. It makes sense. It reduces congestion, and it maximally utilizes space.
We’re interested to learn more — details were scant — about what the government’s thoughts are on this new housing hub that’s being proposed as a division of B.C. Housing. We are unsure of what this goal is, but it seems essential that a new supply would meet the needs of the communities that are seeking new supply. We assume the housing hub will actually work to ensure government investment matches community needs in some way or another. Again, looking forward to the details coming up with that.
Coming to where we’re a little concerned, and what we’re again looking for information for, is the issue of security and safety for renters. Where it says: “government will introduce stronger protections for renters and owners of manufactured homes, and protections for renters facing eviction due to renovation or demolition.” Now again, clearly, there are some very high-profile cases where seniors or others are being evicted for so-called renovictions for a simple paint and shuffle so that rents can be jacked up.
Clearly, we share the concern of government in that regard. However, again, one has to be very careful in introducing legislation that one doesn’t hurt the good landlords and, actually, doesn’t stop them from being able to continue to rent. As we know, if you start to put more and more regulations on housing rentals, we may start to drive that stock out of the rental market — unless it’s done carefully.
There comes a point when someone says: “It’s just not worth the hassle. I’ll hold this, but I’m not going to rent it, because if I rent it, my rent is so controlled that it’s going to cost me $10K when the tenant moves out, and now I can’t reap that.” One has to be very, very, very careful with this.
At the same time, we do have forms of renovictions going on now. We have demovictions going on now in the heart of Burnaby, near the Kingsgate Mall, where low-lying three-story apartment buildings are being condemned left, right and centre. It’s going on now as we speak — right now — in downtown Kelowna as land assemblies are being made in downtown Kelowna. Along Cambie Street in Vancouver, it’s one big land assembly.
This sounds like, “Okay, we’re going to end up building rental accommodation or condos or whatever,” but when you displace these people and you just hold these properties for land assembly, you are creating affordability issues.
The city of Burnaby is in crisis from a rental perspective. High-end condos are replacing low-lying affordable rental units with no plan in place to actually deal with the displaced people. This is a crisis.
Sure, it brings in lots of money through development fees, etc., and through taxes to municipal coffers, but it creates a social problem that we have to get a handle on. So we’re looking forward to seeing what, as the government talks about introducing the housing measures, how it’s going to deal with issues like this — with issues like presales of condominiums and others offshore.
One of the things that we’re delighted to see in this throne speech is a very positive step forward. It’s a positive step forward that we tried to pressure, as did the now government of the former government, to take steps to remedy.
That is the inability, at present, of colleges and universities across British Columbia to build student housing on their campuses without incurring public debt. There are so many potential…. There are people waiting across British Columbia, whether it be Camosun College in my riding, University of Victoria in my riding, UBC, Simon Fraser, Kwantlen College…. Capilano has no housing. The ability for these institutions to build housing on campus will take students out of the market in larger communities onto campuses, thereby easing pressure, as well, in the larger communities.
We have a captive audience on campuses. We know that if there are creative means of allowing these institutions access to capital, that capital has a clientele that will service it in perpetuity. Those are the students in the institution, and they can do so in a very effective means. So we are pleased to see this.
The government also talks, in the throne speech, about making the largest investment in retrofits and renovation of social housing in B.C. in more than 20 years. Talking about…. These upgrades will reserve much-needed housing stock, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reduce home heating bills.
Now again, cautiously optimistic. But I get a little worried about the amount of money being spent and where that money is going to be coming from. This is why we’re quite excited, as the throne speech mentions the emerging economy task force and the innovation commission, that there is a very real move to invigorate the B.C. economy in areas where we’re leaders not only today but also tomorrow.
But with that, we also recognize that retrofitting creates cottage industries of renewable energy companies, building designers and so forth. We know the previous Premier, prior to the last government, recognized that too through the programs that he and his government introduced that actually spurred growth in a diverse array of the building sector — the clean, green building growth.
It’s a matter of saving money. If you can actually spend 15 percent to build a little bit more, to build a building right now, you’ll amortize that in a few years based on today’s technology. It’s about giving people the ability to do that, and we look forward to seeing how that’s going to come down in weeks ahead.
To the issue of child care. Much has been made about the lack of the word “$10-a-day” in the throne speech. To be honest, that’s a slogan. The actual $10-a day plan was a community plan. That’s what it used to be called. Didn’t have as catchy a slogan. We recognize that child care is an important component both of our platform, the NDP platform and also the Liberal throne speech. That we need investments in this. But the investments must come strategically, not through a slogan but ensuring that we have quality access not only to child care but early childhood education and educators for our next generation, the future of our society.
We see a lot in the throne speech about child care. We’re a little troubled by the lack of discussion in there about early childhood education. Child care is not about building spaces. Child care is also about ensuring that we treat the profession of early childhood educators and child care providers as a valued, high-paying profession in our society.
One of the barriers to actual access to child care is the barrier of actual trade ECEs, because as a society, we seem to think it’s okay to pay slightly above minimum wage to people who are looking after our next generation in the most critical years of their development. We really need to give our head a shake, as a society, if we think and expect a child care provider to earn $15 an hour, and we’re going to get people, the best and brightest, in this profession.
They’ve got to make ends meet. They have to afford bus fare. They have to afford to eat, and it’s tough. So we’re hoping we see not only the creation of spaces but incentive programs that will actually supplement the wages of our early childhood…. Such programs did exist in B.C., and they probably still exist in some, but not to the scale that they’re needed.
We have to recognize that we need to ensure that ECEs, child care providers, are viewed, like teachers, as the most important profession in our society. What sort of society are we if we don’t view as our number one priority the education of our next generation, who are the next generation that will take care of us as we age, the next generation that will discover the cure for cancer, the next generation that will find the innovation to ensure that B.C.’s economy is competitive internationally. That is why in the last election we campaigned on investing more than $4 billion over four years into both public education as well as early childhood education and child care.
You know, we have a present system in child care whereby access is a problem. Let’s suppose I’m a low-income person and I want to get access to a child care space. I have to pay up front, and at the end of the year when I file my tax return, I get my child care tax credit back. I don’t need the money then. I needed it to pay my fees up front.
That is why one of the innovative ways that we put in our platform was actually to change the child care tax credit into a child care taxable benefit. That is, money up front isn’t a barrier, but if you earn below a certain amount and you access that child care, it’s viewed as a taxable benefit. Let those who pay and those who want to pay and have the ability to pay, pay.
As Karen Isaac, executive director of B.C. Aboriginal Child Care Society, said:
“Given the long history of Aboriginal children being forcibly removed from their families and communities to residential schools and current high numbers of Aboriginal children being taken into government care, it is no wonder that some poverty-stricken families may be ambivalent about government child care programs and see it as another type of policing over children and their families.”
We must be particularly careful as to how we implement and roll out our child care strategies in Indigenous communities in British Columbia. Our view of what appropriate child care is — when I say “our,” the majority of members in this House — is not the same view as many, many Indigenous communities across British Columbia.
Indigenous communities have a rich history…. Frankly, rich is the wrong word. They have a sordid history of having their children taken from their families, of being forced to have their children taken to schools that they did not intend to go to. So we look forward to seeing how this will play out in the days and weeks ahead.
We’re also keen to see that government is looking to create more child care spaces. But there was some worry, again, in the language of the throne speech where we talk about a main focus on changing unlicensed to licensed providers. That’s important. We want our children to be looked after — licensed providers. But that’s not the only thing we need to focus on.
Obviously, this so-called Baby Mac law will be critical in terms of dealing with issues that led to the tragic death of baby Mac in 2017. However, we must remember that it’s not only about creation of space, and it doesn’t just mean converting unlicensed to licensed. It also means attracting new people into the profession by paying them well, by ensuring that societies value this through education and by working with employers to help facilitate employers actually building child care and early childhood education programs in their corporations and places.
There was a lack of focus of early childhood education in the throne speech. To us, our view is that child care is not only about babysitting; it’s about education. When a child is growing from those early years through to puberty and adulthood, they are very much influenced by the surroundings about them. We hope, as we discuss the child care plan moving forward, that we recognize and reflect upon not only the rights of Aboriginal people but also the importance of education in child care.
I’m very pleased that in the throne speech we hear a focus on poverty reduction. The B.C. Liberals have acknowledged that they’ve stopped listening to British Columbians about the importance of poverty reduction; about the importance of the growing disparity between those who have and those who don’t; and about, from a purely fiscal point of view, the fact that it costs society when this disparity grows in terms of the services that have to be provided.
You eliminate poverty, you eliminate the needs for a lot of social services designed to actually deal with poverty. This is why a housing-first strategy is the preferred approach by so many poverty advocates and why it has been so successful in jurisdictions in the United States where it’s been implemented.
You promote a housing-first strategy…. You cannot deal with issues of mental health and substance abuse unless you get someone in a home, a safe, stable place to be. Once they’re there, these other issues can be dealt with.
In doing so, you save from the judicial system, you save in the hospital system, the medical system, you save in the health care system, you save in the welfare system. You give people housing first. We hope that we a move towards that as this government continues to deliver on its throne speech.
We’re thrilled with the discussion of the B.C. Human Rights Commission and the fact that it’ll be rejuvenated. We’re delighted with the report that was recently released by the Fair Wages Commission, alluded to in the throne speech. Again, $15 was a slogan. How do we get there is what matters, and what do we do beyond that?
We strongly support the recommendations of the Fair Wages Commission to become an established entity in perpetuity in this jurisdiction in order to take politics out of this decision-making and setting minimum wage.
We also look forward to seeing what some of these labour code changes are going to look like. We have little detail, again, and much rhetoric in the throne speech. Good words — I’m not criticizing the words. But some of the details we await to see and look forward to exploring those with our colleagues on both sides of this House.
Now, coming to the economy. I am absolutely delighted and our caucus is delighted with the focus in this throne speech on what B.C. can be leaders at or are leaders at.
I take the example of the forest industry. This is one of our strategic strengths. We have, in British Columbia, three things that no one else in the world can compete with us with. Number one, we are the most beautiful place in the world to live. I get nods over there from the members opposite. Number two, we have one of the best education systems in the world. I got nods there from the former Minister of Education. International assessments year after year have B.C. at the top.
I also have nods over here from another minister. There’s a collegiality here. It’s Valentine’s Day. We’ve all got to get on.
It’s a strategic strength. We know that we can offer employers some of the most highly skilled and educated workers in the world. And, because of our environment, we can attract and retain them here because it’s the most beautiful place to live.
But we also have access to boundless forests, wood, energy in renewable forms and water. These are our strategic strengths that it’s recognized within this throne speech that we can build on as we move towards a sustainable, diverse economy of the 21st century.
We can actually race to the bottom and try to play that game, but we will lose that game. If I dig dirt out of the ground in B.C., there’s a cost that we internalize here. We value our social programs. We value the importance of a minimum wage. We value our environment. It costs a little more to dig the dirt out of the ground here compared to, say, some place like Indonesia, where the same environmental and social costs are not internalized as part of the cost of doing business.
We can compete by trying to do a race for the bottom and forget our values. This is what we’ve been doing with LNG — I’ll come back to that in a second — or we can recognize that the way we compete, the way we grow our GDP, is through more efficient means of doing it, by bringing our technology sector together with our resource sector.
We rely on Finnish technology in our forest sector because Finland recognized that bringing its forestry sector together with its technology sector would lead to innovation, in terms of more efficient extraction, as well as the ability to sell the knowledge and the technology associated with that efficiency.
We have, in British Columbia, some world-leading companies. One of my favourites is MineSense. MineSense is a B.C.-based company that is, at the rock face, able to determine whether or not its efficient to ship rock and crush it or lay it aside. This is a means and ways of extracting mining in much more efficient ways, more clean ways, more green ways that allows us to compete not only in the pure mineral extraction but through the technology that we’ve done.
This throne speech recognizes that our strengths are not in racing to the bottom, but in the fact that we are smarter, and we can attract and retain the best and the brightest.
Let me give you another example: Structurlam. Structurlam is an incredible Penticton-based value-added forest company that makes CrossLam and glulam, replacements for steel and concrete. An 18-storey student residence at UBC is being built from 100 percent wood, CrossLam and glulam products.
Portland has a facility being built there from B.C. products — CrossLam and glulam. Alberta. Across B.C. The Harbour Air terminal. These are beautiful value-added products that actually employ hundreds of people and use B.C. wood, family-based wood. They have a partnership with the Kalesnikoff family out in Nelson to provide some of their lumber.
This is where we succeed. Why do we need to ship a raw log to Korea or to China? China and Korea don’t need raw logs. They need lumber. They need value-added products, and if we bring technology together with our resource sector, we can do so more efficiently because the shipping is minimal in terms of the overall cost.
It’s the same, coming back to the pipeline. Why are we shipping diluted bitumen? Why are we even talking about shipping diluted bitumen to Asian markets? Frankly, I don’t even know that there’s an economic case for Kinder Morgan as it stands, because the largest supplier was going to be California, which now is going to get access to its upgraded products from the Keystone XL that’s just been approved.
Nevertheless, why would we ship those jobs offshore? This isn’t good for the Canadian economy. This isn’t good for jobs. Those jobs get shipped offshore, and what’s worse, we are now building a construction facility in Vancouver airport to import jet fuel. So rather than making the jet fuel here in British Columbia or in Alberta, we ship those jobs off and reimport. That’s the race to the bottom that I think we need to move away from.
And coming to LNG, we’ve had four years of this race to the bottom. This race to the bottom where we’ve tried so desperately to land the impossible that we literally gave away the farm. We’re not going to earn any royalties of any value or substance from natural gas for many, many years because of the deep-well credits where there was at least…. It’s more now, but there was $3.2 billion of unclaimed tax credits against future royalties because of the deep-well credits, which were designed back in the day when it was kind of costly to get deep vertical drills going. Since then, everyone’s got horizontal drilling, costs have come down and, what’s worse, is the previous government then jacked up the credits to shallow wells as well. So we’re not going to earn any money on royalties.
Where will we earn this LNG money, which, fortunately, we’re not focusing on in this throne speech? Well, we’d earn it in the LNG income tax. Oh, no. Capital costs are coming in there. The income tax is cut. We offer below-market electricity, ratepayer-funded Site C to deliver electricity into LNG. You know, literally, we give away the farm.
Landed costs of LNG in Asia years from now…. It was four bucks and change a few months back. I don’t know what it is exactly. It’s gone up a bit — probably six bucks and change. It costs us four bucks to get it out of the ground here in B.C. We can sell it for $2.50 at Chetwynd. It costs us about 11 bucks landed to actually sell it in China. How is it going to happen? How is it going to happen? What business case is it that a company is going to make a major investment here in British Columbia to lose money in every Btu of natural gas they produce?
Louisiana already has the infrastructure on the coast down there, and they already are taking up any supply gaps that existed. The Isthmus of Panama was recently widened. Russia has 20 times the total reserves of all of Canada, and it’s conventional gas, not shale gas, and they’ve signed contracts in and around Asia.
China is now a seller of contracts because they’re oversupplied. We’ve got Australia not bringing onshore stuff that was almost ready to go because there’s no demand, and we think that this is going to be the direction for prosperity in British Columbia. What makes me sad are the false promises that were made by this B.C. Liberal government before us to the people of British Columbia. False hope, undelivered hope. And now the continued pressure to try to deliver the impossible, while recognizing that so many other opportunities are there and we’re missing out on them.
I’d like to take us back to March 3 of 2015. March 3 of 2015 was when I sat across, again, saying — I’ve been saying this since 2012 — “LNG is not going to happen because the market is not there for it.”
On March 3, 2015, 2015, the then Minister of Natural Gas said: “You didn’t do your research. You don’t know what you’re talking about. I know the status of discussions. I know when the final investment decisions are coming. I know the way the companies are planning on making those. I will enjoy the meal to watch the member opposite eat his words in the next year or two.” This was 2015. “I will enjoy watching him eat his words as final investment decisions come that are coming down the pike and he sees the construction of LNG.”
A couple of months later he says: “I want to be invited to the dinner when he has to eat those words. It will happen in the not too distant future, I believe.”
It’s 2018, three years now, and still nothing. The fact that the members opposite think that they have any credibility on any aspect of the economy is mind-boggling, especially since…. What Finance Minister errs to the tune of $2.8 billion in a financial outlook? That’s reckless indifference to the actual economy, as opposed to fine stewardship of the economy. We know where that money came from: an out-of-control real estate sector and the construction industry that’s supporting it. But that’s not a healthy economy. That leads to a boom-and-bust economy, which is why it’s so critical that we diversify.
We look at the place of Terrace, British Columbia, for example. Rather than saying we’re going to try to squeeze LNG, like everyone else is doing, we could be asking: “What is it that you have in Terrace that no one else in the world can compete with?” Let me tell you what they have. They have the first three things we talked about: beautiful place, quality of education and access to resources. But they’re also on a railway line between Prince Rupert and Chicago — the gateway to Asia and the gateway to the eastern U.S.
Why is it we always focus on the raw and not the upgrade or manufacture? Terrace has an amazing opportunity, as a jurisdiction, to try to attract manufacturing there. Why did BMW go to Washington? Why did BMW build a factory in Washington to construct carbon fibre components for their i3 electric vehicles? Because they had access to clean, renewable energy, a stable workforce that they could attract and retain. Where was B.C. in these discussions? Chasing the natural gas unicorn or pot of gold at the end of the rainbow that kept moving. That should have been in Terrace.
Prince George. Let’s look at Prince George. What’s its strategic strength? It’s cold in Prince George right now, and they’ve got a ton of snow. I don’t know whether the member for Cariboo North was able to make it here today. But I know that the member…. We had some difficulty in a committee meeting, because he was snowed in up in the region. But that’s a strategic strength, because that means it’s cold. Why is it that data distribution centres are being built in the U.S.? They should be built in Prince George, because we know the single biggest cost to data distribution is cooling. It’s cooling, and when it’s a cooler place, it costs less. What’s the barrier? Not the speed of light, on which information is transferred. The barrier is lack of access to broadband redundancy.
In British Columbia, historically we’ve thought it’s industry’s role to build fibre and broadband capacity into communities. Now, it’s great that industry has made these investments. But it’s very difficult for a company, a strategic global company, to want to move into a community where its only access to broadband is owned through another company. That’s uncertainty. There’s a role for government, and we’re delighted to see this in the throne speech.
There’s a role for government to create highways — not only bridges and roads that we drive trucks and cars on but also highways for information that everyone has access to, and we’re delighted to see some of that appear in the throne speech.
One of the things that the throne speech mentioned with respect to the forest industry — again, very supportive of the issue with respect to upgrading and value added…. This is one of our key areas. I was troubled by some of the statements there about getting the most value out of affected timber, in cooperation with communities, industry and First Nations.
One has to be very, very careful about how you define value. Is it short-term or long-term? The quickest way to desertify, to make into a desert, large parts of the Cariboo region is to cut down all those burnt trees, which are important for rejuvenation of the next generation of forests.
Again, I would urge government to ensure that they consult not only with communities, industry and First Nations but with scientific experts who have an understanding about forest rejuvenation, particularly academics who have done studies on this and can show you examples of where, if you cut down all the burnt trees, all you leave behind is a forest because the nutrients that were there to actually create the next generation of growth are gone. I hope government’s careful with this as it moves forward.
I’m really excited, in the throne speech, not only about the mention of the innovation commissioner and the emerging economy task force, both of which we campaigned on, but about the opportunity this brings.
I’ve met with Alan Winter twice now, the innovation commissioner, and I can say that British Columbia is so absolutely lucky to have a man of his calibre, of his strengths, of his connections, to be our champion for the innovation sector in British Columbia. I look forward to him taking the programs that exist in Ottawa and matching them with B.C. programs to ensure efficiency and delivery of support to our innovation sector.
He’s concerned about the fact that what happens in British Columbia is companies grow and then move to the States. He’s concerned about creating the environment that will allow companies to grow and remain here in British Columbia.
We have examples of where we’ve tried this. We have a very troubling example right now playing out in B.C. with Bardel Entertainment, one of British Columbia’s top digital media companies, one of the world’s top — a company that set up an office in Kelowna, because of regional and distance tax credits, to try to bring the tech industry out of Vancouver into other parts of British Columbia. When all of a sudden, $5 million was pulled retroactively in the flick of a finger in an amendment that we didn’t debate.
When I tried to raise some issues here, I was told we have to pass it now because the Lieutenant-Governor is coming tomorrow. Five million dollars it cost that industry.
So I hope that we actually start to reflect upon the importance of this sector and the diversity of the sector across British Columbia, so that we nurture and then grow our innovation here in B.C. and don’t ship and export the talent elsewhere as well as the jobs elsewhere.
I’m delighted…. Again, this was a B.C. Liberal commitment in the election campaign, supported and adopted by both the B.C. NDP and by us. The creation of engineering programs across British Columbia.
We know that if you don’t train in an area, you often get sucked into the big metro areas of Vancouver and Victoria. The expansion of the engineering program in Prince George was a great thing for the diversity of our economy across this province. We’re thrilled to see that a total of 2,900 new tech-related spaces at colleges will be created as part of the throne speech over the years to come.
To the issue of reconciliation, the throne speech talks about this government beginning — across ministry framework — to meet our commitments to the United Nations declaration of the rights of Indigenous peoples, the calls to action of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission and the Tsilhqot’in decision.
Obviously, we support this, and we support the government as we move to reconciliation in partnership with First Nations. But let me tell you, there is suspicion, because Indigenous communities — First Nations across our province — are sick and tired of words. I resonate with that. As a climate scientist who spent 25 years in the area, I am sick and tired of hearing governments promise, “We’ll reduce emissions by some amount sometime in the future,” and then not delivering or taking the steps to do it.
What matters to Indigenous communities is not the words. It’s the action. So let’s start to show real action sooner than later as we move towards, truly, truth and reconciliation in this province.
You know, the throne speech also talks about services to people under the areas of health care, education and so forth. Again, we’re excited about the focus in this throne speech away from corporate donors and large entities but towards people and small business. The focus on bringing together family doctors, nurse practitioners and nurses in a community-based approach is one that we think not only the medical community, but certainly our caucuses across this party, can come to agreement on.
I look at the Oceanside Health Centre in Parksville-Qualicum as a success story. The only problem with Oceanside Health Centre is not the way it’s set up, but the growing demand so that its wait times have increased and increased, because it’s a retirement community in there. But it shows a model of the future. But it requires us to think innovatively about how we have billing in the medical profession.
Doctors — there are shortages, no doubt.
But many of today’s doctors do not want to follow the path, particularly in light of the growing bureaucracy that exists in the health care system of having to run their own small business if they’re a family practitioner.
You know, any doctor who owns a family practice will spend, they’ll tell you, at least one day of the five in a week doing administration. Doctors want to be doctors. Young doctors today value the importance of quality in life, as the whole millennial generation do. So thinking about innovative ways of delivering health care through salaried positions, through allowing nurse practitioners to actually bill through the creation of teams, is something that we strongly support — and, in fact, campaigned on — and look forward to seeing the details of as this is fleshed out in the months and years ahead.
In terms of education, again, we see the commitment to fully fund class size and composition requirements: “more than 3,500 new teachers, librarians and counsellors are in B.C. schools, helping students learn in smaller classes with more individual attention.” We see this statement in the throne speech.
It’s quite unfortunate the way this has rolled out, as we know that we shouldn’t have actually ever been in this place to begin with, frankly. If we had not taken steps to take our teachers representatives to court multiple times, all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada, we wouldn’t be in a situation where suddenly we have to hire thousands of teachers in the space of a few months, creating chaos, frankly, in many, many school districts — and within the child care and early childhood education system, where schools are scrambling for spaces and trying to actually meet the legally required commitments.
You know, the throne speech talks about building schools. It talks about removing portables. It talks about seismic upgrades. That’s fine. But let me tell you, what matters in education is not the colour of the wallpaper or the size of the ceilings. What matters is the quality of the teacher and the resources that teacher has in the classroom, as well as the ability for a child to have access to the services they need when they need it.
What we need in British Columbia is enhanced resources in the classroom. Why is it that teachers across British Columbia…? Hon. Speaker, as a former teacher, this must resonate with you too. Why is it that teachers have to spend their own money to provide the actual tools that their children have to use in the classroom? We don’t ever account for that.
Hon. J. Sims: I want to know the answer to that.
A. Weaver: One of the…. I forget which riding you’re….
Hon. J. Sims: Surrey-Panorama.
A. Weaver: Thank you. The member for Surrey-Panorama…. There are all these ridings in Surrey, and they’re all close to each other. They keep changing, because the population’s growing so fast, and I forget who represents which riding.
The member — the minister — pointed out that she wants to know the answer to that. Why is it as a society we don’t recognize what northern European nations recognize, that the single most important profession in our society is education? It’s teachers, early childhood educators, child care providers. These are the people who train the next generation of citizenship. These are the people who create the innovators of tomorrow through providing them skills to actually learn and constructively think.
We seem to think, somehow, that’s it’s okay to pick on our teachers, and that culture needs to change. I’m hoping, with this new government and the direction we’re seeing, that we’ll actually do that. Not only building schools — that’s nice — but actually giving teachers the support they need in the classroom.
Frankly, one of the biggest costs to the education system, and one of the biggest costs to the society, is the fact that something towards 50 percent of teachers don’t continue on after five years, because they’re thrown into situations without the support they need, without the resources they need, to deliver the curriculum that B.C. has, and it’s just unwieldy.
So we have survival of the fittest. We’ll, some of that’s okay, but think of the investment that we have done as a society into training those teachers to get them to the position that they’re delivering in the classroom.
Look at any school district, at the number of people who are on long-term disability because of the unwieldy conditions that they have to work in — the lack of support they’re given. These are costs to society. These are costs that we pay for. If we think of prevention, creating the environment that allows teachers to thrive, we actually save money in the long term.
I’m excited about where we’re heading with teaching. I hope to continue to push the government to ensure that it’s not only about seismic upgrades, but it’s also about giving teachers the resources they need in the classroom to deliver the curriculum.
We’ve done remarkably well in the international PISA assessments, but we also have one of the highest rates of independent schools. Victoria used to have the highest rate of independent schools in the province. We’ve got to value our public education, because that’s our future. Let’s hope we continue down that area.
The throne speech talks about public safety. It talks about important areas in mental health. It talks about a lot of issues in that regard. Again, my concern with the mental health focus in the throne speech is not the importance of harm prevention, but the importance of where we need to invest is not only in stopping people from dying but also to ensure that they’re not there in the first place and that there’s a pathway to recovery at the end.
Anyone who has spoken to firefighters or first responders anywhere in British Columbia will know that it’s not an uncommon story for a first responder to resuscitate the same person multiple times in a day, whether that person be in an emergency room, be a firefighter or a paramedic. That’s a cost.
Providing more access to naloxone…. Sure, it will stop people from dying, but it actually doesn’t deal with the problem. Why is it that people are there in the first place? To what extent are we dealing with the social problems in this province as a direct consequence of our K-to-12 system not having the access and resources that teachers needed in the early, formative years of children to actually ensure that society didn’t have people aging out into these situations? To what extent would we have been avoiding this had we actually given the children the resources they need at the first onsets of diagnosis?
Good luck in British Columbia trying to get a child psychologist in a school district for your child. Those who have will go private, but those who are less fortunate have to wait and wait and wait. In many cases, early intervention would have led to savings in terms of outcomes down the road.
What about recovery? Housing first. It’s good to see the move towards talking about enhanced recovery facilities and also prevention. But it really needs to be our focus, and we continue to hope that government will move down in that regard.
To conclude, I’d like to deal with the issue of climate. In 2012, after being asked four times and finally agreeing to run as an MLA with the B.C. Green Party…. And let me tell you — and to my colleague Robert Stupka, who is running in Kelowna West— it is not the easiest pathway to the B.C. Legislature to run with the B.C. Green Party, particularly when no one had been elected before. You’ve got to work hard.
But when I ran in 2012, I ran because I had spent years in universities teaching. I spent years talking about climate. People and students would ask me: “What can I do?” I’d say: “There are three things you can do. Number one is: you can use your wallet. Each and every one of us has a wallet, and we send a signal to the market by the way we spend. If we buy more efficient products, more locally produced products, that’s the direction the market will head.
We only have to look at the organic food sections in grocery stores. That was a direct response to societal demand. When I was a kid, you would have gone bankrupt if you had an organic food department in your grocery store, because no one would’ve wanted to pay it. Now people are willing to pay a little bit more such that we’re at a stage where the price difference is negligible between organic or non-organic. That’s the power of the pocketbook.
There’s also the power of voting. We live in a democracy, and we have a system in place where we need to put this issue, if it’s important to you, front and centre in decision-making.
That is why, when I talk to students, I also put up the chart showing youth turnout in elections. Historically, in B.C., it was 30 to 40 percent of youth voting and 70 to 80 percent of seniors over the age of 65. Cynically, you can see why people campaign on reducing hip and knee replacement lineups, because you know you’re catering to an audience that will vote, and you can make a very real effect on their lives such that, three years later, you can point to what you’ve done and say: “Look. I listened to you. I reduced those lineups. Vote me back in.” And you know 70 to 80 percent of seniors will vote.
If you’re someone with a vision, like the former Premier of this province, Gordon Campbell, and you bring in place policy measures that you will never reap the benefits of yourself…. We know that socioeconomic inertia is such that the warming we have in store over the next couple of decades is a direct consequence of past decisions, and the decisions we make today will not actually affect those who make the decisions, but it’ll affect the next generation and after. When leaders like Gordon Campbell stand up and make that a priority, they need to be supported, and you need to vote people in who have that vision.
Invariably, these students…. Or in public lectures, people would say: “Oh, these politicians. They’re all the same. All they want to do is line their pockets. They’re in it for power. They’re all corrupt.” Then you can say, and I did: “Well, if you don’t like it, run yourself, because this is the system we’ve got.” It’s a lot better than anarchy, frankly, although some Libertarian candidates may disagree. It’s a lot better than anarchy, and I’d say: “If you don’t like it, run yourself. Find someone to run.”
You can only do that for a few years before you really take a look in the mirror and say: “Really? Am I offering this advice? I’m no different from anyone else. Do as I say and not as I do.” In running with the B.C. Greens — if anyone is interested, you can see it; we had a documentary filmmaker there to follow the campaign — I didn’t think I was going to win. But for me it was a matter of principle, because I could not look my students or, frankly, my family in the face and continue to say one thing and then do another.
When it came to see this throne speech, when it came to our discussions after the last election, you can rest assured that the reason why I was thrilled to actually agree to a confidence and supply agreement with the B.C. NDP, the reason why I am thrilled to see this in the throne speech, is that British Columbia is now repositioning itself to take advantage of not only the challenge but the opportunities that arise from this challenge as we move towards the 21st-century new economy, in terms of diversifying it and moving to the clean, low-carbon economy. But I’m the first to say — and my Indigenous friends have many centuries of this; I have a few decades — that I’m fed up with words. What I want to see is action.
I look forward to working with this government in the months and years ahead as we develop a pathway that actually recognizes that dealing with climate change is the greatest economic opportunity British Columbia has ever had. Because of our strategic strengths, with the most beautiful place in the world to live, one of the best education systems in the world and the ability to access boundless energy, timber, fibre and water, we can position ourselves to move ahead. So bring that in together with the innovation commission and the emerging economy task force. This is a really exciting time for British Columbia.
Now, we can be very cynical here — I get that there are political games, and people want to get in power — or we can recognize this is what it is. It’s a minority government where, I would say, every member in this place ran because they wanted to make British Columbia a better place for all British Columbians. We can actually do that.
My commitment, my caucus’s commitment to both sides of this House, is that we genuinely want to advance good public policy. We want to work with opposition and advance good amendments. We want to be given the courtesy of actually being able to have the time to reflect upon these amendments rather than having them spring upon us on the floor and then sending out tweets and press releases saying: “B.C. Greens Side With MLA.” That’s politics.
People in British Columbia are sick of that. They want us to work together. Whatever happens tonight in Kelowna, I look forward to working with the winner in Kelowna, whether that winner is Ben Stewart, Shelley Cook or Robert Stupka, or — wouldn’t it be interesting? —whether that self-described pit bull is the B.C. Conservative Party candidate in that riding. We’d like to work with all of them, and this place would be much the better for it if we do.
With that, hon. Speaker, I’m delighted to stand in support of the throne speech. I look forward to fulfilling the goals met in the throne speech, and I look forward to seeing, over the weeks ahead, the details emerge as we debate a budget and then the bills that accompany it.
Video of Speech
Responding to government spill response measures
Today the BC Government announced its second phase of regulations to improve preparedness, response and recovery from potential spills. As part of this announcement, restrictions have been put in place to ensure that there will be no increased transport of diluted bitumen (dilbit) in British Columbia until the fate and behaviour of a dilbit spill is better understood scientifically and there is adequate ability to clean up such a spill.
My colleagues and I are very pleased with this announcement. Those who have been following developments on this file will know that I spent an enormous amount of time serving as an intervenor as part of the National Energy Board hearings on the Transmountain pipeline expansion. In fact, in December 2013, we called on the then BC Liberal government to impose a moratorium on dilbit transport on our coast due to the inadequacy of British Coumbia’s spill response and uncertainty in the scientific understanding of fate and behaviour of a dilbit spill. This was further emphasized in my final argument, oral testimony and open letter to Prime Minister Trudeau.
Below I reproduce the press release that we issued in support of the government’s announcement.
Media Release
Weaver responds to government spill response measures
For immediate release
January 30, 2018
VICTORIA, B.C. – Andrew Weaver, leader of the B.C. Green Party, responded today to Minister George Heyman’s announcement that the government is proposing additional measures to protect our environment and coastal waters from heavy oil spills.
“I am pleased to see Minister Heyman putting evidence and science front and centre in government decision-making where it belongs,” said Weaver.
“In particular, I welcome the independent scientific advisory panel that will be established to assess whether regulations can mitigate the impact of heavy oil spills in our precious coastal waters. Our coastal waters provide significant economic activity for our province and the entire country, be it from tourism, fishing or real estate, and are of great cultural significance to First Nations. It is essential that they be adequately protected.
“For several years my office participated extensively in the NEB hearing process for the TransMountain pipeline. We presented evidence from two independent expert assessments that validated our evidence by making it abundantly clear that we simply to not know enough to properly assess the risk and potential damages associated with a diluted bitumen spill in the Salish Sea.
“I look forward to the new panel providing complete, robust and accurate information on this matter to the Minister that reinforces what which we already know – that there is no way currently to adequately respond to a spill of diluted bitumen.
“Furthermore, I am pleased that the government will examine important issues like response times, geographically-specific response needs for our diverse province and compensation for loss of public and cultural use of land, resources or public amenities. B.C. has a rich history of sustainable natural resource development, but it must be done in a way that benefits British Columbians. We must ensure that we are not putting our economy and our communities at risk.”
Weaver was the only MLA to intervene as an individual in the National Energy Board hearings on the TransMountain pipeline expansion. His office was an active participant in the NEB hearing process and submitted a comprehensive report outlining major issues with the spill response regime. Adam Olsen, now Green Party MLA for Saanich North and the Islands, also intervened as a member of the Tsartlip First Nation.
-30-
Background:
The reports referenced above are:
- The Royal Society of Canada Expert Panel Report entitled: The Behaviour and Environmental Impact of Crude Oil Released in Aqueous Environments;
- The US National Academy of Science’s report entitled: Spills of Diluted Bitumen from Pipelines: A Comparative Study of Environmental Fate, Effects, and Response.
Media contact
Jillian Oliver, Press Secretary
+1 778-650-0597 | jillian.oliver@leg.bc.ca
Before it’s too late: British Columbia needs a science- and ecosystem-based approach to wildlife management
At the time of European contact, wildlife were so abundant in British Columbia that early explorers marveled at the richness of the land.
“The country is so crowded with animals as to have the appearance in some places, of a stall yard,” Alexander Mackenzie wrote in his journal in 1793 while on the Peace River. He reported seeing herds of elk on the grasslands near Bear Flat, the irreplaceable habitat that will be drowned when the Site C dam is constructed.
Just over a decade earlier, on the West Coast of Vancouver Island, Captain James Cook noted an abundance of sea otters. He traded pelts into China, sparking a rush for furs that didn’t abate until sea otter populations crashed. It was the first example, in what would become known as British Columbia, of economic forces eradicating a species.
Early European settlers established markets not only for furs, but also for the hides and meat of wildlife. The uncontrolled harvesting that followed soon led to the extirpation of Roosevelt Elk on the Lower Mainland and Wood Bison in northern B.C.
By the late 1800’s wildlife losses were so widespread the public began demanding an end to the free-for-all. In 1859 the first ordinances “providing for the protection of game” were passed in B.C. In 1905 the government organized wildlife management, establishing the Department for the Protection of Game and Forests, although it didn’t get funding until 1908. The annual budget: $10,000.
In 1933 Aldo Leopold, an American conservationist and writer, published Game Management, a book that has been credited with creating the discipline of wildlife management through the application of scientific principles. Indeed, his work planted the seeds of what would eventually become the North American Model of Wildlife Conservation.
One of the key tenets of the Model, which is now widely applied across the continent, is that science – not the dictates of special interest groups – should guide wildlife policy.
I have dedicated my life to understanding our world and its problems through science, but have been surprised at how difficult it is to convince governments to consistently follow scientific reasoning. While the concept of science-based wildlife management has generally been endorsed in B.C. it has not always been applied.
There have been successes. Sea Otters are making a comeback, elk herds are increasing in southern B.C. and bison were successfully reintroduced to some areas in the north. But its selective use has lead to more disasters.
Many wildlife populations are in jeopardy today. Mountain caribou are facing extirpation, wild salmon – a foundation species – are in shocking decline, spotted owls are virtually extinct, and moose populations, which many rural families rely on for sustenance, are in trouble across the province.
What we find in almost all of these instances is that there has been inadequate science, particularly concerning cumulative impacts, and that an unacceptable loss of vital habitat has occurred. The management of wildlife, and the application, or not, of scientific principles, continues to stir great controversy and emotional debate in B.C. Understandably so.
Wildlife management conflicts in which species are pitted against one another are truly challenging, but I have always maintained that humans – elected representatives in particular – have a moral obligation to prevent endangered species from going extinct.
Often, extreme situations are created because government has failed to act. They are typically situations that – for a variety of industrial, social, or budgeting excuses – have been allowed to escalate far past a point of simpler intervention.
When you start rationalizing culling one species to protect another you also introduce an ethical element that needs to be considered alongside scientific findings. Let one – or both – of those species become threatened or endangered, however, and your situation becomes immensely worse.
Some say that humans should not interfere with nature, but sadly, intervention is sometimes necessary. Simply put, many ecosystems have been altered so drastically that we can no longer just stand by and let nature take its course.
If we don’t continue to intervene with the mountain caribou crisis we are currently facing, for example, it will not be long before the remaining herds in the South Selkirk and Peace regions are extirpated.
We cannot let that happen.
Predator control, hunting closures, and restrictions that stop industries from undertaking resource developments are all difficult matters for governments to deal with.
But things aren’t going to get easier. The management of wildlife is becoming increasingly complex and fraught with risk.
Habitat loss is mounting.
The human population is growing.
Roads and pipelines have been spreading into the farthest reaches of the province, and researchers have discovered how such developments increase predation, shift wildlife distribution, and impact abundance.
Wolves, for example, use road and pipeline clearings to get a good line of sight on caribou, expanding into new territory to more efficiently track down their prey. Increased road densities and human activity in wilderness areas elevates human-caused mortality of grizzly bears and reduced the number of bears in the area, scientists at the University of Alberta have recently found.
In a paper published this week in the journal Conservation Biology, scientists wrote about threats to biodiversity from cumulative human impacts in B.C., “one of North America’s last wildlife frontiers.”
“Land-use change is the largest proximate threat to biodiversity yet remains one of the most complex to manage,” they wrote. “For ecosystems, we found that bunchgrass, coastal Douglas fir, and ponderosa pine have been subjected to over 50% land-use conversion, and over 85% of their spatial extent has undergone either direct or estimated indirect impacts.”
Adding to all these other stressors now is climate change. The full implications aren’t yet clear, but we cannot situate our wildlife strategies in the past. Our environment is changing and will continue to do so.
We must be prudent and precautionary as we manage our changing landscape as the planet warms. The timing and abundance of food availability, for instance, will shift for some plants and animals. Species reliant on their stability will need space and additional resources if they are to adapt.
Another challenge that will become increasingly present in B.C. is that of invasive species. Not species introduced from a faraway land, though that will continue to be an issue, but species that have migrated from nearby landscapes as their own native environment ceases to meet their needs — climate refugees, in a sense.
As certain areas become warmer, for example, native species may start to move north. How will we manage those newcomers if they are having a negative impact on our own resident species? What if the invasive species are threatened or endangered in their home ecosystem?
 A few years ago, with concerns growing about how B.C. was managing wildlife in the face of growing pressures, the B.C. government assigned an MLA to do a comprehensive review of its policies.
A few years ago, with concerns growing about how B.C. was managing wildlife in the face of growing pressures, the B.C. government assigned an MLA to do a comprehensive review of its policies.
“There has never been a time in British Columbia’s history where balancing the cumulative impact of resource development and biodiversity has been so complex.” Liberal MLA Mike Morris wrote in his 2015 report, Getting the Balance Right: Improving Wildlife Habitat Management in British Columbia.
“There is an urgency and heightened concern amongst resident hunters, guide outfitters, trappers, the wildlife viewing industry and conservationists that the province is not acting quickly enough to address the decrease in wildlife populations and the degradation of wildlife habitat,” Morris wrote.
He called for more wildlife management staff and “better planning, better science and more timely and effective implementation of policies and programs.”
But the government never delivered.
“B.C. balks at changing law to protect wildlife and biodiversity” said The Vancouver Sun headline.
“The B.C. government will not be changing laws or considering hiring more staff as recommended in a report by one of its own MLAs on how to protect wildlife and biodiversity from the effects of resource industries,” the story said.
For far too long government has shortchanged wildlife management in B.C.
It’s fine for Ministers to say they support science-based decisions – but where is the science? Where are the field researchers? Where are the basic boots on the ground that are needed to keep a close watch on our wildlife populations and habitat?
The necessary funding just isn’t there.
B.C. ranks behind its neighbours in the northwest when it comes to investment in wildlife management. Alberta, Washington, Montana, Oregon, Idaho, Utah – all spend more on managing less.
The shameful underfunding of wildlife management has taken place under successive Liberal regimes. Now we have a new NDP government, but it has yet to show if it will fully embrace – and fund – science-based management.
The problem is compounded because Ottawa too has been cutting back on wildlife science. In B.C. our wild salmon stocks are in decline, putting in jeopardy not only the economies of fishing communities, but also the health of killer whales, bears, eagles and other predators.
But a study published recently concluded, “there is inadequate information to determine the biological status of roughly one-half of all CUs ” in B.C.
CUs, or Conservation Units, are the system by which the federal government is supposed to monitor and manage our wild salmon stocks.
But Canada’s Wild Salmon Policy: an assessment of conservation progress in British Columbia reports that the government just basically gave up on collecting the data. We don’t know what is happening on the rivers because the government stopped keeping track.
“Our state of knowledge regarding salmon populations is eroding rapidly. Without increased support for escapement surveys and the transfer of knowledge to the next generation, the rich legacy of population data available for BC’s north and central coasts is at serious risk of becoming irrelevant for future assessments of management and conservation status,” states the study led by Simon Fraser University researchers Michael Price and John Reynolds.
B.C. is Canada’s most ecologically diverse province but if we are to maintain that rich biodiversity, we need to see a serious commitment to science-based, evidence-based wildlife management – and we need to have dedicated wildlife funding put in place, so managers have the budgets, and the staff, required to do the job.
As the Select Standing Committee on Finance and Government Services recommended in its Report on the Budget 2017 Consultations, license fees collected from natural resource users (hunters, anglers, ecotourists, etc.) should be directed into conservation and wildlife management services, rehabilitation, enforcement and education. In that, we must “prioritize and fund restoration and protection of endangered fresh and saltwater fish species and fisheries.”
Effective natural resource management is reliant on funding, science, and social support. We seem to have consensus on this within the B.C. government, but it needs to be put into action.
Prior to the election, I campaigned on establishing a Natural Resource Commissioner who could lead a Natural Resources Board responsible for establishing sustainable harvest and extraction levels and reporting on the state of B.C.’s environment and natural assets. The NRB, I proposed, would conduct cumulative impact assessments, and oversee the professional reliance model.
Since the election, the government has been working with us to improve the professional reliance model and B.C.’s environmental assessment process. We haven’t talked about creating a Natural Resource Commissioner position, but there is much we should to advance its values of scientific monitoring, reporting, and cumulative assessment.
Managing wildlife has always been difficult, but never more so than now, in the face of climate change. According to data released by scientists at NASA, 2017 was the second warmest year since record-keeping began in 1880, second only to 2016.
In the face of great challenges, it is clear to me that we need a comprehensive science- and ecosystem-based approach to wildlife management. We simply cannot continue to perpetuate the slow, methodical extirpation of native species in B.C.
Ecosystem-based management calls for natural resources, habitat, and species to be managed collectively, over a long time frame, rather than just looking at a single sector or single species.
Cumulative impacts are assessed – an approach which B.C. urgently must follow because of the sweep of industrial development now taking place in many sectors of the province.
Given the myriad challenges facing wildlife in our province, two of the best things we can do to protect biodiversity is to leave key habitat areas intact and fund environmental science. As the global climate warms and precipitation patterns shift, having a complete ecosystem within which animals and plants can try to adapt will be essential, and frankly it is the least we can do given the dire situation many species are in. Having an informed understanding of the changes taking place will help too.
It won’t be easy. But proactively protecting ecosystems – so we can all be resilient to the changes a warming climate will bring – is vital.
British Columbia ends the grizzly bear hunt
Today the BC Government announced a moratorium on the hunting of Grizzly bears in British Columbia. As you can see from our media release reproduced below, we are delighted with the BC NDP announcement.
Media Release
B.C. Green caucus responds to the end of the grizzly bear hunt
For immediate release
December 18th, 2017
VICTORIA, B.C. – “After years of work on this file, my colleagues and I are absolutely overjoyed this decision has finally been made. The results of the government’s consultation were clear and government has listened – we couldn’t be more thrilled,” said Adam Olsen, MLA for Saanich North and the Islands and B.C. Green Party spokesperson for the Ministry of Forests, Lands, Natural Resource Operations and Rural Development.
“A focus on protecting grizzlies has been a constant throughout my time at the legislature, and I am proud to have been able to help advance this issue,” said Andrew Weaver, MLA for Oak Bay-Gordon Head and Leader of the B.C. Green Party.
“Andrew has been a strong advocate for the long term wellbeing of grizzlies since his election in 2013,” said MLA Olsen. “He tabled the Wildlife Amendment Act multiple times and stood as a lone voice in the legislature against the B.C. Liberals who actively supported grizzly trophy hunting and the B.C. NDP who would not take a position. This legislation was intended to give the BC Liberal government a feasible path forward to protecting Grizzly Bears.
“Now we have a very different political landscape in B.C. and our office shifted its efforts accordingly,” said MLA Olsen, who became lead on this file after the May election. “The minority government and a governing agreement signed by the B.C. NDP and B.C. Greens have allowed us to take a stronger position and we commend the government’s bold announcement today.
“Ending the grizzly hunt is a momentous accomplishment, but there is still work to be done to protect this species. If we fail to also consider habitat and food supply – especially with climate change further threatening essential salmon and huckleberry stocks – conflicts with humans, roadkill rates, or poaching incidents, we will fail to protect grizzlies in the long term.
“We hope that this announcement will be followed with a comprehensive ecosystem based approach to wildlife management because we cannot continue to perpetuate the slow, methodical extirpation of native species in BC. We will celebrate progress along the way and work to ensure species like grizzly bears and wild pacific salmon have the resilient ecosystems they need to thrive into the future.
“This breakthrough would not have happened without the efforts of many – thank you and congratulations to everyone involved.”
-30-
Media contact
Sarah Miller, Acting Press Secretary
+1 778-650-0597 | sarah.miller@leg.bc.ca